Selective Detection of Nano-Sized Diagnostic Markers Using Au-ZnO Nanorod-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) in Ureteral Obstruction Models
- PMID: 33122904
- PMCID: PMC7589161
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S272500
Selective Detection of Nano-Sized Diagnostic Markers Using Au-ZnO Nanorod-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) in Ureteral Obstruction Models
Abstract
Background: This study investigated the diagnosis of renal diseases using a biochip capable of detecting nano-sized biomarkers. Raman measurements from a kidney injury model were taken, and the feasibility of early diagnosis was assessed.
Materials and methods: Rat models with mild and severe unilateral ureteral obstructions were created, with the injury to the kidney varying according to the tightness of the stricture. After generating the animal ureteral obstruction models, urine was collected from the kidney and bladder.
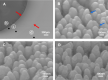
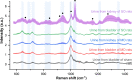
Results and discussion: After confirming the presence of renal injury, urine drops were placed onto a Raman chip whose surface had been enhanced with Au-ZnO nanorods, allowing nano-sized biomarkers that diffused into the nanogaps to be selectively amplified. The Raman signals varied according to the severity of the renal damage, and these differences were statistically confirmed.
Conclusion: These results confirm that ureteral stricture causes kidney injury and that signals in the urine from the release of nano-biomarkers can be monitored using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
Keywords: ZnO nanorods; nano-sized biomarker; principal component analysis; renal injury; surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy; ureteral obstruction.
© 2020 Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests and no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures



References
-
- El-Ghar ME, Shokeir AA, El-Diasty TA, Refaie HF, Gad HM, El-Dein AB. Contrast enhanced spiral computerized tomography in patients with chronic obstructive uropathy and normal serum creatinine: a single session for anatomical and functional assessment. J Urol. 2004;172(3):985–988. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000135368.77589.7c - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

