Cetuximab-Coated Thermo-Sensitive Liposomes Loaded with Magnetic Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for Targeted EGFR-Expressing Breast Cancer Combined Therapy
- PMID: 33122906
- PMCID: PMC7591010
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S261671
Cetuximab-Coated Thermo-Sensitive Liposomes Loaded with Magnetic Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for Targeted EGFR-Expressing Breast Cancer Combined Therapy
Abstract
Background: One major limitation of cancer chemotherapy is a failure to specifically target a tumor, potentially leading to side effects such as systemic cytotoxicity. In this case, we have generated a cancer cell-targeting nanoparticle-liposome drug delivery system that can be activated by near-infrared laser light to enable local photo-thermal therapy and the release of chemotherapeutic agents, which could achieve combined therapeutic efficiency.
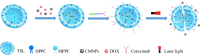
Methods: To exploit the magnetic potential of iron oxide, we prepared and characterized citric acid-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (CMNPs) and encapsulated them into thermo-sensitive liposomes (TSLs). The chemotherapeutic drug, doxorubicin (DOX), was then loaded into the CMNP-TSLs, which were coated with an antibody against the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), cetuximab (CET), to target EGFR-expressing breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo studies in mouse model.
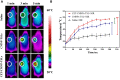
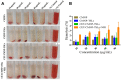
Results: The resulting CET-DOX-CMNP-TSLs were stable with an average diameter of approximately 120 nm. First, the uptake of TSLs into breast cancer cells increased by the addition of the CET coating. Next, the viability of breast cancer cells treated with CET-CMNP-TSLs and CET-DOX-CMNP-TSLs was reduced by the addition of photo-thermal therapy using near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation. What is more, the viability of breast cancer cells treated with CMNP-TSLs plus NIR was reduced by the addition of DOX to the CMNP-TSLs. Finally, photo-thermal therapy studies on tumor-bearing mice subjected to NIR laser irradiation showed that treatment with CMNP-TSLs or CET-CMNP-TSLs led to an increase in tumor surface temperature to 44.7°C and 48.7°C, respectively, compared with saline-treated mice body temperature ie, 35.2°C. Further, the hemolysis study shows that these nanocarriers are safe for systemic delivery.
Conclusion: Our studies revealed that a combined therapy of photo-thermal therapy and targeted chemotherapy in thermo-sensitive nano-carriers represents a promising therapeutic strategy against breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; cetuximab; combined therapy; doxorubicin; epidermal growth factor receptors; iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles.
© 2020 Dorjsuren et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

