Overexpression of hsa_circ_0001715 is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33122916
- PMCID: PMC7591015
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S274932
Overexpression of hsa_circ_0001715 is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play important roles in tumorigenesis, including lung cancer. However, the expression profile and clinical value of circRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma remain unclear. The purpose of this study was to establish the circRNAs expression profile of lung adenocarcinoma and determine its potential diagnostic and prognostic value.
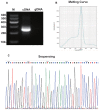
Materials and methods: The global expression profile of circRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma tissue was determined from five paired lung adenocarcinoma tissues and adjacent normal tissues. The expression levels of selected candidate circRNA were validated by qRT-PCR. Sequence analysis was used to confirm the specificity of amplified circRNA. The candidate circRNA level was further detected in plasma samples from lung adenocarcinoma patients and healthy controls. The relationships between their levels and clinicopathological factors were explored. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed to differentiate lung adenocarcinoma from healthy controls. Kaplan-Meier was performed to show survival curves and survival characteristics. The significance of different prognostic factors for overall survival (OS) was analyzed using Cox proportional hazards model.
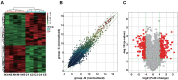
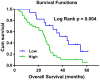
Results: CircRNA microarray showed 394 circRNAs were differentially expressed, including 215 up-regulated and 179 down-regulated circRNAs. Hsa_circ_0001715 was the most up-regulated circRNA in lung adenocarcinoma tissues. Plasma hsa_circ_0001715 levels were significantly higher in lung adenocarcinoma patients versus healthy controls (P < 0.001). We further found that high plasma hsa_circ_0001715 was significantly correlated with TNM stage (P = 0.039) and distant metastasis (P = 0.030). Furthermore, ROC curve analysis showed that hsa_circ_0001715 had high diagnostic value, and the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.871. Lung adenocarcinoma patients with plasma hsa_circ_0001715 levels over 0.417 had significantly shorter OS than those with lower levels (P = 0.004). Univariate and multivariate survival analysis showed that plasma hsa_circ_0001715 level was an independent prognostic factor for the OS.
Conclusion: Our study revealed an aberrant circRNA expression profile in lung adenocarcinoma, and hsa_circ_0001715 is up-regulated and could act as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: biomarker; circular RNA; hsa_circ_0001715; lung adenocarcinoma tissues; prognosis.
© 2020 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

