Transmitted and Acquired HIV-1 Drug Resistance from a Family: A Case Study
- PMID: 33122923
- PMCID: PMC7591230
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S272232
Transmitted and Acquired HIV-1 Drug Resistance from a Family: A Case Study
Abstract
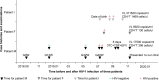
Antiretroviral drug resistance has become a major threat to the adequate management of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, but little attention has been paid to the spread and evolution of drug-resistant strains in the family. Here, we described a case of transmitted as well as acquired HIV drug resistance among a father, mother and infant. Epidemiological data were obtained retrospectively. Drug resistance mutations (DRMs) of three patients were tested using a validated In-house Sanger-based sequencing (SBS) method and the Vela next-generation sequencing (NGS) platform. Gene evolution analysis was also performed. According to the epidemiological history and phylogenetic data, in late pregnancy of the mother, the infant's father transmitted HIV-1 to her, and then the mother to the baby, leading to the transmission of V106I as a common mutation of three persons. The mutant frequency was 99.57% (father), 95.38% (mother) and 99.73% (infant), respectively. Mother also acquired K101E (41.03%), K103N (27.56%) and minor mutation of V106M (4.30%) after improperly discontinuing antiretroviral regimen of lamivudine (3TC), tenofovir (TDF) and efavirenz (EFV). Such acquired mutations increased the drug resistance scores on non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) doravirine, EFV, etravirine, nevirapine and rilpivirine from 10, 0, 10, 10 and 10 to 65, 135, 25, 150 and 55, respectively. Therefore, sexually transmitted diseases, especially DRMs of HIV-1 in families, are of concern and draw attention to the need for enhanced drug-resistance prevention efforts, and accurate surveillance by more sensitive methods in complicated cases.
Keywords: HIV-1; drug resistance; minor mutation; next-generation sequencing; sexually transmitted diseases.
© 2020 Yan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. HIV drug resistance report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/drugresistance/hivdr-report-2019/en/. Accessed December22, 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases