Imrecoxib Inhibits Paraquat-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through the NF- κ B/Snail Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33123215
- PMCID: PMC7582077
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6374014
Imrecoxib Inhibits Paraquat-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through the NF- κ B/Snail Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Objective: In recent years, pulmonary fibrosis caused by paraquat poisoning is still concerned. However, no effective drugs have been developed yet to treat paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis. The aim of our research is to investigate whether imrecoxib can inhibit paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis and its possible mechanism.
Methods: Extraction of primary pulmonary fibrosis cells (PPF cells) in vitro by the method of trypsin digestion. RT-qPCR and western blot were employed to measure the transcription level and protein expression of EMT related markers in paraquat-induced A549 cells. MTT, wound-healing, and Transwell experiments were used to verify the effect of imrecoxib on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of PPF and HFL1 cells.
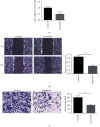
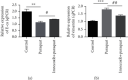
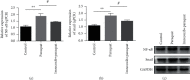
Results: Firstly, our results confirmed that paraquat can induce EMT and activate the NF-κB/snail signal pathway in lung epithelial cell A549. Furthermore, experimental results showed that imrecoxib could repress the proliferation, migration, and invasion of PPF and HFL1 cells. Finally, our study found that imrecoxib can inhibit EMT of paraquat-induced A549 cells by the NF-κB/snail signal pathway.
Conclusion: Imrecoxib can inhibit EMT of paraquat-induced A549 cells and alleviate paraquat-caused pulmonary fibrosis through the NF-κB/snail signal pathway. Therefore, imrecoxib is a drug worthy of study in the treatment of paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Copyright © 2020 Haihao Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ji Y., Wang T., Wei Z. F., et al. Paeoniflorin, the main active constituent of Paeonia lactiflora roots, attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by suppressing the synthesis of type I collagen. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2013;149(3):825–832. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.08.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim K. K., Kugler M. C., Wolters P. J., et al. Alveolar epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2006;103(35):13180–13185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605669103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

