Bardoxolone Methyl Displays Detrimental Effects on Endothelial Bioenergetics, Suppresses Endothelial ET-1 Release, and Increases Endothelial Permeability in Human Microvascular Endothelium
- PMID: 33123312
- PMCID: PMC7584962
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4678252
Bardoxolone Methyl Displays Detrimental Effects on Endothelial Bioenergetics, Suppresses Endothelial ET-1 Release, and Increases Endothelial Permeability in Human Microvascular Endothelium
Abstract
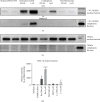
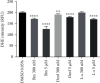
Nrf2 is a master regulator of antioxidant cellular defence, and agents activating the Nrf2 pathway have been tested in various diseases. However, unexpected side effects of cardiovascular nature reported for bardoxolone methyl in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and stage 4 chronic kidney disease (the BEACON trial) still have not been fully explained. Here, we aimed to characterize the effects of bardoxolone methyl compared with other Nrf2 activators-dimethyl fumarate and L-sulforaphane-on human microvascular endothelium. Endothelial toxicity, bioenergetics, mitochondrial membrane potential, endothelin-1 (ET-1) release, endothelial permeability, Nrf2 expression, and ROS production were assessed in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) incubated for 3 and 24 hours with 100 nM-5 μM of either bardoxolone methyl, dimethyl fumarate, or L-sulforaphane. Three-hour incubation with bardoxolone methyl (100 nM-5 μM), although not toxic to endothelial cells, significantly affected endothelial bioenergetics by decreasing mitochondrial membrane potential (concentrations ≥ 3 μM), decreasing spare respiratory capacity (concentrations ≥ 1 μM), and increasing proton leak (concentrations ≥ 500 nM), while dimethyl fumarate and L-sulforaphane did not exert such actions. Bardoxolone methyl at concentrations ≥ 3 μM also decreased cellular viability and induced necrosis and apoptosis in the endothelium upon 24-hour incubation. In turn, endothelin-1 decreased permeability in endothelial cells in picomolar range, while bardoxolone methyl decreased ET-1 release and increased endothelial permeability even after short-term (3 hours) incubation. In conclusion, despite that all three Nrf2 activators exerted some beneficial effects on the endothelium, as evidenced by a decrease in ROS production, bardoxolone methyl, the most potent Nrf2 activator among the tested compounds, displayed a distinct endothelial profile of activity comprising detrimental effects on mitochondria and cellular viability and suppression of endothelial ET-1 release possibly interfering with ET-1-dependent local regulation of endothelial permeability.
Copyright © 2020 Ewa Szczesny-Malysiak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Mandal A., Bishayee A. Trianthema portulacastrum Linn. displays anti-inflammatory responses during chemically induced rat mammary tumorigenesis through simultaneous and differential regulation of NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015;16(2):2426–2445. doi: 10.3390/ijms16022426. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

