IFN- γ Mediates the Development of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 33123584
- PMCID: PMC7586164
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7176515
IFN- γ Mediates the Development of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect all organs in the body. It is characterized by overexpression of antibodies against autoantigen. Although previous bioinformatics analyses have identified several genetic factors underlying SLE, they did not discriminate between naive and individuals exposed to anti-SLE drugs. Here, we evaluated specific genes and pathways in active and recently diagnosed SLE population.
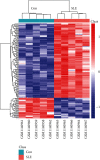
Methods: GSE46907 matrix downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) was analyzed using R, Metascape, STRING, and Cytoscape to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs), enrichment pathways, protein-protein interaction (PPI), and hub genes between naive SLE individuals and healthy controls.
Results: A total of 134 DEGs were identified, in which 29 were downregulated, whereas 105 were upregulated in active and newly diagnosed SLE cases. GO term analysis revealed that transcriptional induction of the DEGs was particularly enhanced in response to secretion of interferon-γ and interferon-α and regulation of cytokine production innate immune responses among others. KEGG pathway analysis showed that the expression of DEGs was particularly enhanced in interferon signaling, IFN antiviral responses by activated genes, class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC-I) mediated antigen processing and presentation, and amyloid fiber formation. STAT1, IRF7, MX1, OASL, ISG15, IFIT3, IFIH1, IFIT1, OAS2, and GBP1 were the top 10 DEGs.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that interferon-related gene expression and pathways are common features for SLE pathogenesis, and IFN-γ and IFN-γ-inducible GBP1 gene in naive SLE were emphasized. Together, the identified genes and cellular pathways have expanded our understanding on the mechanism underlying development of SLE. They have also opened a new frontier on potential biomarkers for diagnosis, biotherapy, and prognosis for SLE.
Copyright © 2020 Wenping Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Tsokos G. C. Systemic lupus erythematosus. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2011;22(365):2110–2121. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

