Double-Targeted Knockdown of miR-21 and CXCR4 Inhibits Malignant Glioma Progression by Suppression of the PI3K/AKT and Raf/MEK/ERK Pathways
- PMID: 33123586
- PMCID: PMC7584940
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7930160
Double-Targeted Knockdown of miR-21 and CXCR4 Inhibits Malignant Glioma Progression by Suppression of the PI3K/AKT and Raf/MEK/ERK Pathways
Abstract
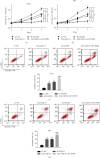
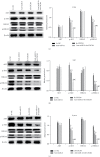
Currently, miR-21 and CXCR4 are being extensively investigated as two key regulators in glioma malignancy. In this study, we investigated the combined effects of these two factors on glioma progression. Herein, the expression of miR-21 and CXCR4 was increased in tumor tissues and cell lines. Inhibition of miR-21, CXCR4, and miR-21 and CXCR4 together all reduced the migration, invasiveness, proliferation, and enhanced apoptosis in glioma cells, as well as reduced tumor volume and mass in xenograft model. The inhibition effect was strongest in double-targeted knockdown of miR-21 and CXCR4 group, whose downstream pathways involved in AKT axis and ERK axis activation. In conclusion, our findings reported that double-targeted knockdown of miR-21 and CXCR4 could more effectively inhibit the proliferation, migration, invasion, and growth of transplanted tumor and promote cell apoptosis, which were involved in the PI3K/AKT and Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2020 Feijiao Liu and Bo Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures




References
-
- Yang X. J., Long H. A., Sheng-ping Y. U. Study on invasion and migration of malignant glioma. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Neurology & Neurosurgery. 2018;18(1):p. 36.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

