Vasculitis changes in COVID-19 survivors with persistent symptoms: an [18F]FDG-PET/CT study
- PMID: 33123760
- PMCID: PMC7595761
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-020-05084-3
Vasculitis changes in COVID-19 survivors with persistent symptoms: an [18F]FDG-PET/CT study
Abstract
Purpose: Several patients experience unexplained persistent symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 recovering. We aimed at evaluating if 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose ([18F]FDG) was able to demonstrate a persistent inflammatory process.
Methods: Recovered adult COVID-19 patients, who complained unexplained persisting symptoms for more than 30 days during the follow-up visits, were invited to participate in the study. Patients fulfilling inclusion criteria were imaged by [18F]FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography ([18F]FDG-PET/CT). Whole-body [18F]FDG-PET/CT, performed according to good clinical practice, was qualitatively (comparison with background/liver) and semi-quantitatively (target-to-blood pool ratio calculated as average SUVmax artery/average SUVmean inferior vena cava) analyzed. Negative follow-up [18F]FDG-PET/CT images of oncologic patients matched for age/sex served as controls. Mann-Whitney test was used to test differences between groups. SPSS version 26 was used for analyses.
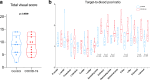
Results: Ten recovered SARS-CoV-2 patients (seven male and three females, median age 52 years, range 46-80) with persisting symptoms were enrolled in the study. Common findings at visual analysis were increased [18F]FDG uptake in bone marrow and blood vessels (8/10 and 6/10 cases, respectively). [18F]FDG uptake in bone marrow did not differ between cases and controls (p = 0.16). The total vascular score was similar in the two groups (p = 0.95). The target-to-blood pool ratio resulted higher in recovered SARS-CoV-2 patients than in controls.
Conclusion: Although the total vascular score was similar in the two groups, the target-to-blood pool ratio was significantly higher in three vascular regions (thoracic aorta, right iliac artery, and femoral arteries) in the recovered COVID-19 cohort than in controls, suggesting that SARS-CoV-2 induces vascular inflammation, which may be responsible for persisting symptoms.
Keywords: Infection; Inflammation; Long COVID; SARS-CoV-2; Vasculitis; [18F]FDG-PET/CT.
Conflict of interest statement
Sollini, Ciccarelli, Morelli, Aghemo, and Gelardi had no conflicts of interest. Cecconi MC reports personal fees from Edwards Lifesciences, Directed Systems, and Cheetah Medical, outside the submitted work. Chiti received speaker honoraria from General Electric and Blue Earth Diagnostics, acted as scientific advisor for Blue Earth Diagnostics and Advanced Accelerator Applications, and benefited from an unconditional grant from Sanofi to Institution. All honoraria and grants are outside the scope of the submitted work.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

