Adduct annotation in liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry to enhance compound identification
- PMID: 33123762
- PMCID: PMC7806579
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-020-03019-3
Adduct annotation in liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry to enhance compound identification
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Adduct annotation in liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry to enhance compound identification.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Feb;413(5):1505. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-03148-9. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33438044 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
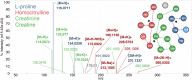
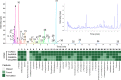
Annotation and interpretation of full scan electrospray mass spectra of metabolites is complicated by the presence of a wide variety of ions. Not only protonated, deprotonated, and neutral loss ions but also sodium, potassium, and ammonium adducts as well as oligomers are frequently observed. This diversity challenges automatic annotation and is often poorly addressed by current annotation tools. In many cases, annotation is integrated in metabolomics workflows and is based on specific chromatographic peak-picking tools. We introduce mzAdan, a nonchromatography-based multipurpose standalone application that was developed for the annotation and exploration of convolved high-resolution ESI-MS spectra. The tool annotates single or multiple accurate mass spectra using a customizable adduct annotation list and outputs a list of [M+H]+ candidates. MzAdan was first tested with a collection of 408 analytes acquired with flow injection analysis. This resulted in 402 correct [M+H]+ identifications and, with combinations of sodium, ammonium, and potassium adducts and water and ammonia losses within a tolerance of 10 mmu, explained close to 50% of the total ion current. False positives were monitored with mass accuracy and bias as well as chromatographic behavior which led to the identification of adducts with calcium instead of the expected potassium. MzAdan was then integrated in a workflow with XCMS for the untargeted LC-MS data analysis of a 52 metabolite standard mix and a human urine sample. The results were benchmarked against three other annotation tools, CAMERA, findMAIN, and CliqueMS: findMAIN and mzAdan consistently produced higher numbers of [M+H]+ candidates compared with CliqueMS and CAMERA, especially with co-eluting metabolites. Detection of low-intensity ions and correct grouping were found to be essential for annotation performance. Graphical abstract.
Keywords: Adducts; Electrospray; HRMS; Liquid chromatography; Metabolomics; Software.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

