Pancreatic solid pseudopapillary neoplasm in male patients: systematic review with three new cases
- PMID: 33123945
- PMCID: PMC8397648
- DOI: 10.1007/s13304-020-00905-4
Pancreatic solid pseudopapillary neoplasm in male patients: systematic review with three new cases
Abstract
Pancreatic solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (pSPN) is a rare exocrine neoplasm, which generally occurs in young women. This study analyses the clinical characteristics of pSPN in male patients through a systematic review of the literature, adding three new cases from our institution. We reviewed our experience in Pspns, and we performed a systematic review of pSPN of all articles published in English in PubMed and SCOPUS from 1980. Using the final included articles, we evaluated clinic-pathological features, surgical treatment and prognosis of male patients affected by pSPN. From the literature review and our cases, we collected 246 male patients with a proven pSPN. Mean age was 34.3 (range 4-78) years, with 26.2% patients younger than 18 years. Patients were asymptomatic in 35.9% of cases, despite a mean tumour size of 6.3 cm. In 63.7% of cases, the pSPN was located in the body-tail region. Distant metastases were reported at diagnosis in only 10 (4.1%) patients. A correct pre-operative diagnosis (including cytopathology) was provided in 53.6% of patients, with only 40 fine-needle aspiration/biopsy performed. Standard pancreatic resections represented 90.4% of surgical procedures. Beta-catenin and progesterone receptors were positive at immunostaining in 100% and 77.8% of cases, respectively. Fourteen (7.2%) patients relapsed after a mean disease-free survival of 43.1 months. After a mean follow-up of 47 (range 4-180) months, 89.5% of patients were alive and disease-free. Although rare, when dealing with a solid-cystic pancreatic mass, even in asymptomatic male patients, a pSPN should be considered as a possible diagnosis.
Keywords: Male patient; Pancreatic surgery; Pancreatic tumour; Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

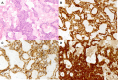
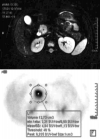
References
-
- Frantz VK. Tumors of the pancreas. In: Bumberg CW, editor. Atlas of tumor pathology. Washington: US Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1959. pp. 32–33.
-
- Klöppel G, Basturk O, Klimstra DS, Lam AK, Notohara K. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas. In: Carneiro F, Chan JKC, Cheung NYA, editors. Digestive system tumours. WHO classification of tumors. Lyon: IARC Press; 2019. pp. 340–342.
-
- Tang LH, Aydin H, Brennan MF, Klimstra DS. Clinically aggressive solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: a report of two cases with components of undifferentiated carcinoma and a comparative clinicopathologic analysis of 34 conventional cases. Am J SurgPathol. 2005;29:512–519. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000155159.28530.88. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

