Burden of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Beyond Erythropoietin
- PMID: 33123967
- PMCID: PMC7854472
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-020-01524-6
Burden of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Beyond Erythropoietin
Abstract
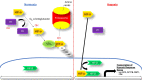
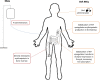
Anemia is a frequent comorbidity of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with a considerable burden because of decreased patient health-related quality of life and increased healthcare resource utilization. Based on observational data, anemia is associated with an increased risk of CKD progression, cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality. The current standard of care includes oral or intravenous iron supplementation, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and red blood cell transfusion. However, each of these therapies has its own set of population-specific patient concerns, including increased risk of cardiovascular disease, thrombosis, and mortality. Patients receiving dialysis or those who have concurrent diabetes or high blood pressure may be at greater risk of developing these complications. In particular, treatment with high doses of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents has been associated with increased rates of hospitalization, cardiovascular events, and mortality. Resistance to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents remains a therapeutic challenge in a subset of patients. Hypoxia-inducible factor transcription factors, which regulate several genes involved in erythropoiesis and iron metabolism, can be stabilized by a new class of drugs that act as inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase enzymes to promote erythropoiesis and elevate hemoglobin levels. Here, we review the burden of anemia of chronic kidney disease, the shortcomings of current standard of care, and the potential practical advantages of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitors in the treatment of patients with anemia of CKD.
Keywords: Anemia; Burden; Chronic kidney disease; Erythropoietin; Hypoxia-inducible factor; Iron; Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:279–335.
-
- Bonomini M, Del Vecchio L, Sirolli V, Locatelli F. New treatment approaches for the anemia of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;67:133–142. - PubMed

