The rising worldwide impact of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 33124118
- PMCID: PMC8170717
- DOI: 10.1111/bju.15286
The rising worldwide impact of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
Objectives: To describe the trend in the impact of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia (LUTS/BPH) on a global scale using the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database.
Materials and methods: Using the GBD database, worldwide data aggregated from registries and health systems from 1990 to 2017 were filtered for LUTS/BPH diagnoses. Calculation of years lived with disability (YLD) were compared with other urological diseases. YLD were calculated by a standardized method using assigned disability weights. The GBD-defined sociodemographic index (SDI) was used to assess impact of LUTS/BPH by global SDI quintile.
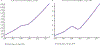
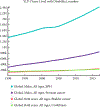
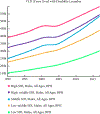
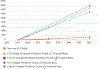
Results: Global Burden of Disease data over the 1990-2017 study period were summarized and global numbers and trends noted with other urological diseases for comparison. A total of 2 427 334 YLD were attributed to BPH in 2017 alone, almost three times more than those attributed to the next highest urological disease, prostate cancer (843 227 YLD). When stratified by SDI quintile, a much lower impact of BPH was found in the bottom three quintiles, despite this subset representing 66.9% of the 2017 world population.
Conclusions: Lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia exert a rapidly rising human burden far exceeding other urological diseases. As the population ages and men in a lower SDI enjoy increased life expectancy and decreased competing mortalities, a continually accelerating wave of LUTS/BPH can be forecast. These epidemiological trends have serious implications for the future allocation of resources and the global urological workforce.
Keywords: #UroBPH; benign prostatic hyperplasia; global health; lower urinary tract symptoms; prostate; quality of life.
© 2020 The Authors BJU International © 2020 BJU International Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
Bryn Launer, William Ricke and Granville Lloyd have nothing to disclose. Kevin McVary declares the following: having served as a scientific study or trial, and principal investigator for NxThera, a principal investigator and consultant for NIDDK and Olympus, a principal investigator for Astellas, a principal investigator and fellowship grant consultant for Boston Scientific (formerly AMS), and being a patent holder for A1 Thermal-Actived Penile Prosthesis.
Figures
References
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol 1984; 132: 474–9 - PubMed
-
- Irwin DE, Milsom I, Hunskaar S et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: results of the EPIC study. Eur Urol 2006; 50: 1306–15 - PubMed
-
- Welch G, Weinger K, Barry MJ. Quality-of-life impact of lower urinary tract symptom severity: results from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. Urology 2002; 59: 245–50 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

