Lack of Consistent Malaria Incidence Hotspots in a Highland Kenyan Area During a 10-Year Period of Very Low and Unstable Transmission
- PMID: 33124534
- PMCID: PMC7695093
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0821
Lack of Consistent Malaria Incidence Hotspots in a Highland Kenyan Area During a 10-Year Period of Very Low and Unstable Transmission
Abstract
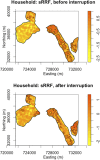
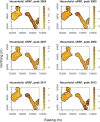
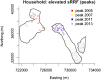
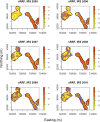
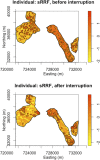
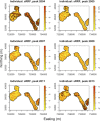
The use of spatial data in malaria elimination strategies is important to understand whether targeted interventions against malaria can be used, particularly in areas with limited resources. We previously documented consistent areas of increased malaria incidence in the epidemic-prone area of Kipsamoite in highland Kenya from 2001 to 2004. In this area and a neighboring subcounty (Kapsisiywa), malaria incidence decreased substantially in 2005, going from peak incidence of 31.7 per 1,000 persons in June 2004 to peak incidence of 7.4 per 1,000 persons in May 2005. Subsequently, the use of indoor residual spraying and artemisinin combination therapy malaria treatment led to a possible interruption of malaria transmission for a 13-month period from 2007 to 2008, after which the incidence returned to very low levels until an epidemic in April-July 2013. In the present study, we used novel kernel density estimation methods to determine whether areas of increased malaria incidence were consistent in six periods of peak incidence from 2003 to 2013, and to assess patterns of incidence in the period before versus. after the period of possible interruption. Areas of highest incidence differed during peak malaria transmission periods over the years 2003-2013, and differed before and after the potential malaria interruption. In this epidemic-prone region with very low malaria transmission, consistent malaria "hotspots" identified in a time of higher transmission are no longer present. Ongoing assessment of spatial malaria epidemiology to identify and target current areas of elevated malaria risk may be important in campaigns to control or eliminate malaria in epidemic-prone areas.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial support: This project was supported by grants from NIH-NIAID (NCT00393757), NIH Fogarty International Center (D43 TW0080085), the University of Minnesota Amplatz Children’s Hospital, and an NIH research training grant (R25 TW009345) awarded to the Northern Pacific Global Health Fellows Program by Fogarty International Center in partnership with several NIH Institutes (NIMH, NIGMS, NHLBI, OAR, and OWH).
Disclosure: This study was published with the permission of the director of the Kenya Medical Research Institute.
Disclaimer: The funding agencies were not involved in any aspect of the study including design, analysis, or interpretation of results.
Figures
References
-
- Summers J, 1989. Soho – A History of London’s Most Colourful Neighborhood. London: Bloomsbury.
-
- Roll Back Malaria Partnership , 2008. The Global Malaria Action Plan. Technical Report. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
-
- Feachem RGA, Phillips AA, Targett GA, editors, 2009. Shrinking the Malaria Map: A Prospectus on Malaria Elimination. San Francisco, CA: The Global Health Group, Global Health Sciences, University of California, San Francisco.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

