Norwich COVID-19 testing initiative pilot: evaluating the feasibility of asymptomatic testing on a university campus
- PMID: 33124664
- PMCID: PMC7665602
- DOI: 10.1093/pubmed/fdaa194
Norwich COVID-19 testing initiative pilot: evaluating the feasibility of asymptomatic testing on a university campus
Abstract
Background: There is a high prevalence of COVID-19 in university-age students, who are returning to campuses. There is little evidence regarding the feasibility of universal, asymptomatic testing to help control outbreaks in this population. This study aimed to pilot mass COVID-19 testing on a university research park, to assess the feasibility and acceptability of scaling up testing to all staff and students.
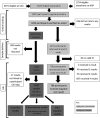
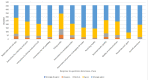
Methods: This was a cross-sectional feasibility study on a university research park in the East of England. All staff and students (5625) were eligible to participate. All participants were offered four PCR swabs, which they self-administered over two weeks. Outcome measures included uptake, drop-out rate, positivity rates, participant acceptability measures, laboratory processing measures, data collection and management measures.
Results: 798 (76%) of 1053 who registered provided at least one swab; 687 (86%) provided all four; 792 (99%) of 798 who submitted at least one swab had all negative results and 6 participants had one inconclusive result. There were no positive results. 458 (57%) of 798 participants responded to a post-testing survey, demonstrating a mean acceptability score of 4.51/5, with five being the most positive.
Conclusions: Repeated self-testing for COVID-19 using PCR is feasible and acceptable to a university population.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Faculty of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Policy Paper: Slides to Accompany Coronavirus Press Conference: 9 September 2020. Prime Minister’s Office, 10 Downing Street. p. 2.
-
- Davies NG, Klepac P, Liu Y et al. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nature Medicine. 2020;26(8):1205–11. - PubMed
-
- Fancourt D, Bu F, Mak H, Steptoe A. Covid-19 social study: results release 17. UCL. 2020;5.
-
- Weeden K, Cornwell B. The small-world network of college classes: implications for epidemic spread on a university campus. Sociological Science. 2020;7(9):222–41.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical