The international glycan repository GlyTouCan version 3.0
- PMID: 33125071
- PMCID: PMC7779025
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa947
The international glycan repository GlyTouCan version 3.0
Abstract
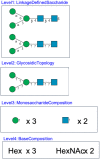
Glycans serve important roles in signaling events and cell-cell communication, and they are recognized by lectins, viruses and bacteria, playing a variety of roles in many biological processes. However, there was no system to organize the plethora of glycan-related data in the literature. Thus GlyTouCan (https://glytoucan.org) was developed as the international glycan repository, allowing researchers to assign accession numbers to glycans. This also aided in the integration of glycan data across various databases. GlyTouCan assigns accession numbers to glycans which are defined as sets of monosaccharides, which may or may not be characterized with linkage information. GlyTouCan was developed to be able to recognize any level of ambiguity in glycans and uniquely assign accession numbers to each of them, regardless of the input text format. In this manuscript, we describe the latest update to GlyTouCan in version 3.0, its usage, and plans for future development.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Varki A., Cummings R.D., Esko J.D., Stanley P., Hart G.W., Aebi M., Darvill A.G., Kinoshita T., Packer N.H., Prestegard J.H. et al. .. Essentials of Glycobiology. 2017; 3rd ednCold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. - PubMed
-
- Aoki-Kinoshita K.F. A Practical Guide to Using Glycomics Databases. 2017; Japan, Tokyo: Springer.
-
- Berners-Lee T., Hendler J.. Publishing on the semantic web. Nature. 2001; 410:1023–1024. - PubMed
-
- Herget S., Ranzinger R., Maass K., von der Lieth C.-W.. GlycoCT – a unifying sequence format for carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Res. 2008; 343:2162–2171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

