Frequency and risk factors for major complications after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors in 1235 ablation sessions: a 15-year experience
- PMID: 33125554
- PMCID: PMC8043912
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07409-0
Frequency and risk factors for major complications after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors in 1235 ablation sessions: a 15-year experience
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the frequency of major complications after multi-probe stereotactic radiofrequency ablation (SRFA) in a large cohort of patients over 15 years and to elucidate risk factors for adverse events.
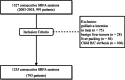
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was carried out between July 2003 and December 2018. Seven hundred ninety-three consecutive patients (median 65.0 years (0.3-88), 241 women and 552 men, were treated in 1235 SRFA sessions for 2475 primary and metastatic liver tumors with a median tumor size of 3.0 cm (0.5-18 cm). The frequency of major complications was evaluated according to SIR guidelines and putative predictors of adverse events analyzed using simple and multivariable logistic regression.
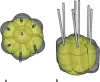
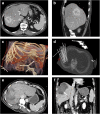
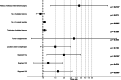
Results: Thirty-day mortality after SRFA was 0.5% (6/1235) with an overall major complication rate of 7.4% (91/1235). The major complication rate decreased from 11.5% (36/314) (before January 2011) to 6.0% (55/921) (p = 0.001). 50.5% (46/91) of major complications were successfully treated in the same anesthetic session by angiographic coiling for hemorrhage and chest tube insertion for pneumothorax. History of bile duct surgery/intervention, number of coaxial needles, and location of tumors in segment IVa or VIII were independent prognostic factors for major complications following multivariable logistic regression analysis. Simple logistic regression revealed the number of tumors, tumor size, location close to the diaphragm, tumor conglomerate, and segment VII as other significant predictors.
Conclusion: SRFA of liver tumors is safe and can extend the treatment spectrum of conventional RFA. Adaptations over time combined with increasing experience resulted in a significant decrease in complications.
Key points: • In 1235 ablation sessions in 793 patients over 15 years, we found a mortality rate of 0.5% (6/1235) and an overall major complication rate of 7.4%, which fell from 11.5 (36/314) to 6.0% (55/921, p = 0.001) after January 2011, likely due to procedural adaptations. • History of bile duct surgery/intervention (p = 0.013, OR = 3.290), number of coaxial needles (p = 0.026, OR = 1.052), and location of tumors in segment IVa (p = 0.016, OR = 1.989) or VIII (p = 0.038, OR = 1.635) were found to be independent prognostic factors. • Simple logistic regression revealed that number of tumors, tumor size, location close to the diaphragm, tumor conglomerates, and segment VII were other significant predictors of major complications.
Keywords: Liver; Neoplasm; Radiofrequency ablation; Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Technical efficacy and local recurrence after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of 2653 liver tumors: a 15-year single-center experience with evaluation of prognostic factors.Int J Hyperthermia. 2022;39(1):421-430. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2022.2044522. Int J Hyperthermia. 2022. PMID: 35227136
-
Safety and efficacy of stereotactic radiofrequency ablation for very large (≥8 cm) primary and metastatic liver tumors.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;10(1):1618. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58383-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32005871 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility, safety, and long-term efficacy of stereotactic radiofrequency ablation for tumors adjacent to the diaphragm in the hepatic dome: a case-control study.Eur Radiol. 2020 Feb;30(2):950-960. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06399-y. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31489472 Free PMC article.
-
Complications of radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: Frequency and risk factors.World J Hepatol. 2014 Mar 27;6(3):107-13. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i3.107. World J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24672640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereotactic Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors: 3D Planning, Multiple Needle Approach, and Intraprocedural Image Fusion Are the Key to Success-A Narrative Review.Biology (Basel). 2021 Jul 10;10(7):644. doi: 10.3390/biology10070644. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Software-based planning of ultrasound and CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in hepatic tumors.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Jun;16(6):1051-1057. doi: 10.1007/s11548-021-02394-1. Epub 2021 May 11. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33974224 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and clinical impact of bile ducts changes after multibipolar radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2024 Sep;34(9):5529-5540. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10617-7. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38334763
-
Percutaneous thermal ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with and without TIPS.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 May;50(5):2294-2303. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04655-4. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39487918
-
Complications Risk Assessment and Imaging Findings of Thermal Ablation Treatment in Liver Cancers: What the Radiologist Should Expect.J Clin Med. 2022 May 13;11(10):2766. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102766. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35628893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Probe RFA vs. Single-Probe MWA in an Ex Vivo Bovine Liver Model: Comparison of Volume and Shape of Coagulation Zones.Biology (Basel). 2023 Aug 8;12(8):1103. doi: 10.3390/biology12081103. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37626989 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

