Computed tomography semi-automated lung volume quantification in SARS-CoV-2-related pneumonia
- PMID: 33125559
- PMCID: PMC7596627
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07271-0
Computed tomography semi-automated lung volume quantification in SARS-CoV-2-related pneumonia
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate a semi-automated segmentation and ventilated lung quantification on chest computed tomography (CT) to assess lung involvement in patients affected by SARS-CoV-2. Results were compared with clinical and functional parameters and outcomes.
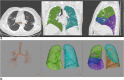
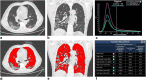
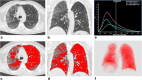
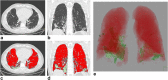
Methods: All images underwent quantitative analyses with a dedicated workstation using a semi-automatic lung segmentation software to compute ventilated lung volume (VLV), Ground-glass opacity (GGO) volume (GGO-V), and consolidation volume (CONS-V) as absolute volume and as a percentage of total lung volume (TLV). The ratio between CONS-V, GGO-V, and VLV (CONS-V/VLV and GGO-V/VLV, respectively), TLV (CONS-V/TLV, GGO-V/TLV, and GGO-V + CONS-V/TLV respectively), and the ratio between VLV and TLV (VLV/TLV) were calculated.
Results: A total of 108 patients were enrolled. GGO-V/TLV significantly correlated with WBC (r = 0.369), neutrophils (r = 0.446), platelets (r = 0.182), CRP (r = 0.190), PaCO2 (r = 0.176), HCO3- (r = 0.284), and PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) values (r = - 0.344). CONS-V/TLV significantly correlated with WBC (r = 0.294), neutrophils (r = 0.300), lymphocytes (r = -0.225), CRP (r = 0.306), PaCO2 (r = 0.227), pH (r = 0.162), HCO3- (r = 0.394), and P/F (r = - 0.419) values. Statistically significant differences between CONS-V, GGO-V, GGO-V/TLV, CONS-V/TLV, GGO-V/VLV, CONS-V/VLV, GGO-V + CONS-V/TLV, VLV/TLV, CT score, and invasive ventilation by ET were found (all p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The use of quantitative semi-automated algorithm for lung CT elaboration effectively correlates the severity of SARS-CoV-2-related pneumonia with laboratory parameters and the need for invasive ventilation.
Key points: • Pathological lung volumes, expressed both as GGO-V and as CONS-V, can be considered a useful tool in SARS-CoV-2-related pneumonia. • All lung volumes, expressed themselves and as ratio with TLV and VLV, correlate with laboratory data, in particular C-reactive protein and white blood cell count. • All lung volumes correlate with patient's outcome, in particular concerning invasive ventilation.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Computed tomography, X-ray; Infection, coronavirus; Lung volume measurements; Pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Two of the authors (M.P. and S.T.) are affiliated with PHILIPS HEALTHCARE, as a specialist product, and they helped and supervised us during the use of COPD Software, without any financial support. The other authors of manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
References
-
- Use of laboratory methods for SARS diagnosis. In: who.int. https://www.who.int/csr/sars/labmethods/en/. Accessed 10 July 2020
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

