(-)-Epicatechin induces mitochondrial biogenesis and markers of muscle regeneration in adults with Becker muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 33125736
- PMCID: PMC7898288
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.27108
(-)-Epicatechin induces mitochondrial biogenesis and markers of muscle regeneration in adults with Becker muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Introduction: We conducted an open-label study to examine the effects of the flavonoid (-)-epicatechin in seven ambulatory adult patients with Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD).
Methods: Seven participants received (-)-epicatechin 50 mg twice per day for 8 weeks. Pre- and postprocedures included biceps brachii biopsy to assess muscle structure and growth-relevant endpoints by western blotting, mitochondria volume measurement, and cristae abundance by electron microscopy, graded exercise testing, and muscle strength and function tests.
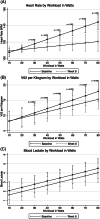
Results: Western blotting showed significantly increased levels of enzymes modulating cellular bioenergetics (liver kinase B1 and 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha, a transcriptional coactivator of genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and cristae-associated mitofilin levels, increased as did cristae abundance. Muscle and plasma follistatin increased significantly while myostatin decreased. Markers of skeletal muscle regeneration myogenin, myogenic regulatory factor-5, myoblast determination protein 1, myocyte enhancer factor-2, and structure-associated proteins, including dysferlin, utrophin, and intracellular creatine kinase, also increased. Exercise testing demonstrated decreased heart rate, maximal oxygen consumption per kilogram, and plasma lactate levels at defined workloads. Tissue saturation index improved in resting and postexercise states.
Discussion: (-)-Epicatechin, an exercise mimetic, appears to have short-term positive effects on tissue biomarkers indicative of mitochondrial biogenesis and muscle regeneration, and produced improvements in graded exercise testing parameters in patients with BMD.
Keywords: aerobic exercise, Becker muscular dystrophy, epicatechin, mitochondrial biogenesis follistatin.
© 2020 The Authors. Muscle & Nerve published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures




References
-
- Timpani CA, Hayes A, Rybalka E. Revisiting the dystrophin‐ATP connection: how half a century of research still implicates mitochondrial dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy aetiology. Med Hypotheses. 2015;85:1021‐1033. - PubMed
-
- Iwabu M, Yamauchi T, Okada‐Iwabu M, et al. Adiponectin and AdipoR1 regulate PGC‐1alpha and mitochondria by Ca(2+) and AMPK/SIRT1. Nature. 2010;464:1313‐1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

