Effects of Coronavirus Disease 2019 on Solid Organ Transplantation
- PMID: 33127076
- PMCID: PMC7491991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.09.006
Effects of Coronavirus Disease 2019 on Solid Organ Transplantation
Abstract
Background: As the novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has emerged as a viral pandemic, data on the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection undergoing solid organ transplant are emerging. The objective of this systematic review was to assess currently published literature relating to the management, clinical course, and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in liver, kidney, and heart solid organ transplant recipients.
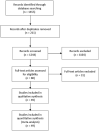
Methods: We conducted a systematic review to assess currently published literature relating to the management, clinical course, and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in liver, kidney, and heart solid organ transplant recipients. Articles published through June 2020 were searched in the MEDLINE, ClinicalTrials.gov, and PubMed databases. We identified 49 eligible studies comprising a total of 403 solid organ transplant recipients.
Results: Older age, male sex, and preexisting comorbidities, including hypertension and/or diabetes, were the most common prevailing characteristics among the solid organ transplant recipients. Clinical presentation ranged from mild to severe disease, including multiorgan failure and death. We found an overall mortality rate of 21%.
Conclusion: Our analysis suggests no increase in overall mortality or worse outcome in solid organ transplant recipients receiving immunosuppressive therapy compared with mortality in the general surgical population with SARS-CoV-2. Our findings suggest that transplant surgery and its immunosuppressive effects should not be a deterrent to proper surgical care for patients in the SARS-CoV-2 era.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Similar articles
-
Clinical Presentation, Treatment, and Mortality Rate in Liver Transplant Recipients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Quantitative Analysis.Transplant Proc. 2020 Nov;52(9):2676-2683. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.07.012. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Transplant Proc. 2020. PMID: 32891405 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Immunocompromised Organ Transplant Recipients: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Transplant Proc. 2020 Nov;52(9):2698-2702. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.07.014. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Transplant Proc. 2020. PMID: 32800516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spectrum of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outcomes in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Single-Center Experience.Transplant Proc. 2020 Nov;52(9):2654-2658. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Transplant Proc. 2020. PMID: 33041077 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: Initial report from the US epicenter.Am J Transplant. 2020 Jul;20(7):1800-1808. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15941. Epub 2020 May 10. Am J Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32330343 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: A single-center case series from Spain.Am J Transplant. 2020 Jul;20(7):1849-1858. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15929. Epub 2020 May 10. Am J Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32301155 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Structured Review of 2020.Transplant Proc. 2021 Oct;53(8):2421-2434. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2021.08.019. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Transplant Proc. 2021. PMID: 34551880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selecting the Next Generation of Surgeons: General Surgery Program Directors and Coordinators Perspective on USMLE Changes and Holistic Approach.World J Surg. 2021 Nov;45(11):3258-3265. doi: 10.1007/s00268-021-06261-7. Epub 2021 Jul 31. World J Surg. 2021. PMID: 34333683 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Post-SARS-COV2 Infectious Complications in Kidney Transplant Recipient.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Sep 29;58(10):1370. doi: 10.3390/medicina58101370. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36295531 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and outcome of coronavirus disease 2019 infection in patients with solid organ transplants: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Infect Public Health. 2022 Mar;15(3):365-372. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Feb 19. J Infect Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35193818 Free PMC article.
-
The association between severe or death COVID-19 and solid organ transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2021 Jul;35(3):100628. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2021.100628. Epub 2021 May 21. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2021. PMID: 34087553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. 2020. https://web.archive.org/web/20200418151429/https://www.who.int/dg/speech... [accessed 29.06.20]
-
- WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=EAIaIQobChMIyN6ygr3k6QIVy8DACh0R6A_HEAAYA... [accessed 04.09.20]
-
- Aziz H., Filkins A., Kwon Y.K. Review of COVID-19 outcomes in surgical patients. Am Surg. 2020;86(7):741–745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous