Highly Sensitive and Specific Multiplex Antibody Assays To Quantify Immunoglobulins M, A, and G against SARS-CoV-2 Antigens
- PMID: 33127841
- PMCID: PMC8111153
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01731-20
Highly Sensitive and Specific Multiplex Antibody Assays To Quantify Immunoglobulins M, A, and G against SARS-CoV-2 Antigens
Abstract
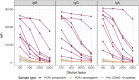
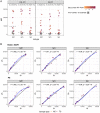
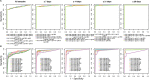
Reliable serological tests are required to determine the prevalence of antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and to characterize immunity to the disease in order to address key knowledge gaps in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Quantitative suspension array technology (qSAT) assays based on the xMAP Luminex platform overcome the limitations of rapid diagnostic tests and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) with their higher precision, dynamic range, throughput, miniaturization, cost-efficiency, and multiplexing capacity. We developed three qSAT assays for IgM, IgA, and IgG against a panel of eight SARS-CoV-2 antigens, including spike protein (S), nucleocapsid protein (N), and membrane protein (M) constructs. The assays were optimized to minimize the processing time and maximize the signal-to-noise ratio. We evaluated their performances using 128 prepandemic plasma samples (negative controls) and 104 plasma samples from individuals with SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis (positive controls), of whom 5 were asymptomatic, 51 had mild symptoms, and 48 were hospitalized. Preexisting IgG antibodies recognizing N, M, and S proteins were detected in negative controls, which is suggestive of cross-reactivity to common-cold coronaviruses. The best-performing antibody/antigen signatures had specificities of 100% and sensitivities of 95.78% at ≥14 days and 95.65% at ≥21 days since the onset of symptoms, with areas under the curve (AUCs) of 0.977 and 0.999, respectively. Combining multiple markers as assessed by qSAT assays has the highest efficiency, breadth, and versatility to accurately detect low-level antibody responses for obtaining reliable data on the prevalence of exposure to novel pathogens in a population. Our assays will allow gaining insights into antibody correlates of immunity and their kinetics, required for vaccine development to combat the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgA; IgG; IgM; Luminex; RBD; SARS-CoV-2; antibody; coronavirus; immunity; immunoassay; multiplex; nucleocapsid; performance; quantitative suspension array technology; sensitivity; specificity; spike.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


References
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. 2020. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382:727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

