Wnt/Beta-catenin/Esrrb signalling controls the tissue-scale reorganization and maintenance of the pluripotent lineage during murine embryonic diapause
- PMID: 33127892
- PMCID: PMC7603494
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19353-0
Wnt/Beta-catenin/Esrrb signalling controls the tissue-scale reorganization and maintenance of the pluripotent lineage during murine embryonic diapause
Abstract
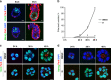
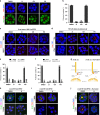
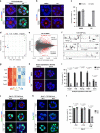
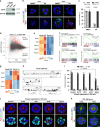
The epiblast, which provides the foundation of the future body, is actively reshaped during early embryogenesis, but the reshaping mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, using a 3D in vitro model of early epiblast development, we identify the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway and its central downstream factor Esrrb as the key signalling cascade regulating the tissue-scale organization of the murine pluripotent lineage. Although in vivo the Wnt/β-catenin/Esrrb circuit is dispensable for embryonic development before implantation, autocrine Wnt activity controls the morphogenesis and long-term maintenance of the epiblast when development is put on hold during diapause. During this phase, the progressive changes in the epiblast architecture and Wnt signalling response show that diapause is not a stasis but instead is a dynamic process with underlying mechanisms that can appear redundant during transient embryogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wnt/β-catenin signalling regulates Sox17 expression and is essential for organizer and endoderm formation in the mouse.Development. 2013 Aug;140(15):3128-38. doi: 10.1242/dev.088765. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Development. 2013. PMID: 23824574
-
Wnt/ß-catenin signalling and the dynamics of fate decisions in early mouse embryos and embryonic stem (ES) cells.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Dec;47-48:101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26321498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential requirements for β-catenin during mouse development.Development. 2012 Oct;139(20):3711-21. doi: 10.1242/dev.085597. Development. 2012. PMID: 22991437
-
Modulation of β-catenin function maintains mouse epiblast stem cell and human embryonic stem cell self-renewal.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2403. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3403. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23985566 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of WNT signaling on tissue lineage differentiation in the early mouse embryo.Dev Growth Differ. 2011 Sep;53(7):843-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2011.01292.x. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Dev Growth Differ. 2011. PMID: 21762130 Review.
Cited by
-
Long Noncoding RNA ACTA2-AS1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Facilitates Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer by Binding with miR-6720-5p to Regulate ESRRB.Biochem Genet. 2023 Dec;61(6):2672-2690. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10399-5. Epub 2023 May 24. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 37222961
-
Poised PABP-RNA hubs implement signal-dependent mRNA decay in development.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Sep;31(9):1439-1447. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01363-x. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39054355 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR activity paces human blastocyst stage developmental progression.Cell. 2024 Nov 14;187(23):6566-6583.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.048. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39332412 Free PMC article.
-
Self-organization of embryonic stem cells into a reproducible embryo model through epigenome editing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 10:2024.03.05.583597. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.05.583597. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Stem Cell. 2025 Jun 5;32(6):895-913.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2025.02.015. PMID: 38496557 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Tissue-intrinsic beta-catenin signals antagonize Nodal-driven anterior visceral endoderm differentiation.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 13;15(1):5055. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49380-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38871742 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

