Association of a dysbiotic oral microbiota with the development of focal lymphocytic sialadenitis in IκB-ζ-deficient mice
- PMID: 33127905
- PMCID: PMC7599236
- DOI: 10.1038/s41522-020-00158-4
Association of a dysbiotic oral microbiota with the development of focal lymphocytic sialadenitis in IκB-ζ-deficient mice
Abstract
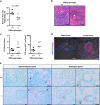
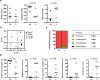
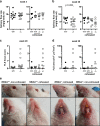
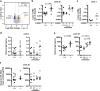
Mice lacking IκB-ζ, a protein encoded by the Nfkbiz gene, spontaneously develop a Sjögren's syndrome-like disease involving the lachrymal glands, but no salivary gland symptoms have been reported. We found that Nfkbiz-/- female mice presented a significantly reduced salivary flow rate, focal lymphocytic sialadenitis (FLS), and a dysbiotic oral microbiota at week 24. To dissect the contributions of genetic and environmental factors to the salivary gland phenotype, Nfkbiz+/+ and Nfkbiz-/- mice were cohoused after weaning and evaluated at week 20. Cohousing alleviated the salivary gland phenotype of Nfkbiz-/- mice but did not induce any disease phenotype in Nfkbiz+/+ mice. Additionally, the oral microbiota in the cohoused mice was synchronized toward that in Nfkbiz+/+ mice. In conclusion, IκB-ζ-deficient mice developed hyposalivation and FLS, in which a dysbiotic oral microbiota played an important role. This finding suggests that the dysbiotic oral microbiota could be a therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dysbiotic oral microbiota and infected salivary glands in Sjögren's syndrome.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 24;15(3):e0230667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230667. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32208441 Free PMC article.
-
Dysbiotic salivary microbiota in dry mouth and primary Sjögren's syndrome patients.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 18;14(6):e0218319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218319. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31211815 Free PMC article.
-
The resident pathobiont Staphylococcus xylosus in Nfkbiz-deficient skin accelerates spontaneous skin inflammation.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 24;7(1):6348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05740-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28740238 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Sjögren's syndrome-like autoimmune lesions in MRL/lpr mice.Pathol Int. 1994 Aug;44(8):559-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1994.tb01716.x. Pathol Int. 1994. PMID: 7952145 Review.
-
The oral microbiome and human health.J Oral Sci. 2017;59(2):201-206. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.16-0856. J Oral Sci. 2017. PMID: 28637979 Review.
Cited by
-
Why Should We Consider Potential Roles of Oral Bacteria in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren Syndrome?Immune Netw. 2022 Aug 3;22(4):e32. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e32. eCollection 2022 Aug. Immune Netw. 2022. PMID: 36081525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental Murine Periodontitis Increases Salivary Gland IgA-Producing B Cells Following Oral Dysbiosis.Microbiol Immunol. 2025 Feb;69(2):114-127. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.13191. Epub 2024 Dec 22. Microbiol Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39709535 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota and Sjögren's syndrome: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 13;14:1187906. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1187906. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37383227 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and Function of the Atypical IκBs-Bcl-3, IκBNS, and IκBζ-in Lymphocytes and Autoimmunity.Eur J Immunol. 2025 May;55(5):e202451273. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451273. Eur J Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40359334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A positive cytokine/chemokine feedback loop establishes plasmacytoid DC-driven autoimmune pancreatitis in IgG4-related disease.JCI Insight. 2024 Sep 12;9(20):e167910. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.167910. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39264798 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

