Proteomics reveals the preliminary physiological states of the spotted seal (Phoca largha) pups
- PMID: 33127980
- PMCID: PMC7599241
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-75759-2
Proteomics reveals the preliminary physiological states of the spotted seal (Phoca largha) pups
Abstract
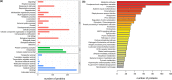
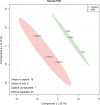
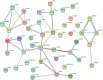
Spotted seal (Phoca largha) is a critically endangered pinniped in China and South Korea. The conventional method to protect and maintain the P. largha population is to keep them captive in artificially controlled environments. However, little is known about the physiological differences between wild and captive P. largha. To generate a preliminary protein expression profile for P. largha, whole blood from wild and captive pups were subjected to a label-free comparative proteomic analysis. According to the results, 972 proteins were identified and predicted to perform functions related to various metabolic, immune, and cellular processes. Among the identified proteins, the expression level of 51 were significantly different between wild and captive P. large pups. These differentially expressed proteins were enriched in a wide range of cellular functions, including cytoskeleton, phagocytosis, proteolysis, the regulation of gene expression, and carbohydrate metabolism. The abundances of proteins involved in phagocytosis and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis were significantly higher in the whole blood of wild P. largha pups than in captive individuals. In addition, heat shock protein 90-beta, were determined as the key protein associated with the differences in the wild and captive P. largha pups due to the most interactions of it with various differentially expressed proteins. Moreover, wild P. largha pups could be more nutritionally stressed and have more powerful immune capacities than captive pups. This study provides the first data on the protein composition of P. largha and provides useful information on the physiological characteristics for research in this species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-Read Sequencing Revealing the Effectiveness of Captive Breeding Strategy for Improving the Gut Microbiota of Spotted Seal (Phoca largha).Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024 Nov 26;27(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s10126-024-10397-7. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024. PMID: 39589560
-
Integrated proteomics and metabolomics reveal the variations in the physiological state of spotted seal (Phoca largha) pups following artificial rescue.Genomics. 2022 Mar;114(2):110282. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110282. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35131476
-
Differences in Heavy Metal Accumulation in Wild and Captive Spotted Seal (Phoca largha) Pups in the Bohai Sea.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70342. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70342. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40323954 Free PMC article.
-
Hair mercury concentrations in the spotted seal (Phoca largha) pups from the Sea of Japan.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Sep;25(27):27133-27140. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2731-6. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30022391
-
On the ecology of the harbour seal Phoca vitulina in the Wadden Sea: population dynamics, residue levels, and management.Vet Q. 1982 Jan;4(1):36-42. doi: 10.1080/01652176.1982.9693836. Vet Q. 1982. PMID: 15861586 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Key Proteins Involved in Testicular Development of Yaks.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 2;25(15):8433. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158433. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126002 Free PMC article.
-
Informatics-assisted proteomics revealing the anti-inflammatory effects of satsuma orange (Citrus unshiu) peel flavonoid extract in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 12;34(5):1207-1218. doi: 10.1007/s10068-025-01830-1. eCollection 2025 Mar. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40093549
-
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Zearalenone Exposure on Uterine Development in Weaned Gilts.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 9;14(10):692. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100692. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287961 Free PMC article.
-
Unstable pathogen profile in spotted seal (Phoca largha) gut microbiota and limited turnover with habitat microbiome.Int Microbiol. 2025 Aug;28(6):1183-1195. doi: 10.1007/s10123-024-00615-6. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Int Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39532804
-
Long-Read Sequencing Revealing the Effectiveness of Captive Breeding Strategy for Improving the Gut Microbiota of Spotted Seal (Phoca largha).Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024 Nov 26;27(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s10126-024-10397-7. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024. PMID: 39589560
References
-
- Gao XG, Han JB, Lu ZC, Zhang PJ, He CBD. novo assembly and characterization of spotted seal Phoca largha transcriptome using Illumina paired-end sequencing. Comp. Biochem. Phys. D. 2013;8(2):103–110. - PubMed
-
- Gardiner KJ, Hall AJ. Diel and annual variation in plasma cortisol concentrations among wild and captive harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) Can. J. Zool. 1997;75(11):1773–1780. doi: 10.1139/z97-806. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

