The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal health due to delay in seeking health care: Experience from a tertiary center
- PMID: 33128794
- PMCID: PMC9087665
- DOI: 10.1002/ijgo.13457
The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal health due to delay in seeking health care: Experience from a tertiary center
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on obstetric care and outcomes.
Methods: A prospective observational single-center study was performed, including all antenatal and parturient women admitted from April to August, 2020. Data were collected regarding number of admissions, deliveries, antenatal visits, reason for inaccessibility of health care, and complications during pregnancy, and compared with data from the pre-COVID period of October 2019 to February 2020.
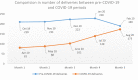
Results: There was a reduction of 45.1% in institutional deliveries (P < 0.001), a percentage point increase of 7.2 in high-risk pregnancy, and 2.5-fold rise in admission to the intensive care unit of pregnant women during the pandemic. One-third of women had inadequate antenatal visits. The main reason for delayed health-seeking was lockdown and fear of contracting infection, resulting in 44.7% of pregnancies with complications. Thirty-two symptomatic women who tested positive for COVID-19 were managed at the center with good maternal and fetal outcomes.
Conclusion: Although COVID-19 does not directly affect pregnancy outcomes, it has indirect adverse effects on maternal and child health. Emergency obstetric and antenatal care are essential services to be continued with awareness of people while maintaining social distancing and personal hygiene.
Keywords: COVID-19; Complications; Delay; Health care; Maternal; Pregnancy.
© 2020 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) Situation report – 44. Published 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default‐source/coronaviruse/situation‐reports/2... itrep44‐COVID‐19.pdf?sfvrsn=783b4c9d_2. Accessed October 8, 2020
-
- WHO . Managing epidemics: key facts about major deadly diseases. Geneva May, 2018. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/managing‐epidemics/interactive.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2020
-
- Elston JW, Cartwright C, Ndumbi P, Wright J. The health impact of the 2014–15 Ebola outbreak. Public Health. 2017;143:60‐70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous