Spotlight on microRNAs in allergy and asthma
- PMID: 33128813
- PMCID: PMC8246745
- DOI: 10.1111/all.14646
Spotlight on microRNAs in allergy and asthma
Abstract
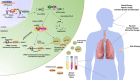
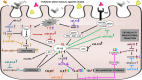
In past 10 years, microRNAs (miRNAs) have gained scientific attention due to their importance in the pathophysiology of allergic diseases and their potential as biomarkers in liquid biopsies. They act as master post-transcriptional regulators that control most cellular processes. As one miRNA can target several mRNAs, often within the same pathway, dysregulated expression of miRNAs may alter particular cellular responses and contribute, or lead, to the development of various diseases. In this review, we give an overview of the current research on miRNAs in allergic diseases, including atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, and asthma. Specifically, we discuss how individual miRNAs function in the regulation of immune responses in epithelial cells and specialized immune cells in response to different environmental factors and respiratory viruses. In addition, we review insights obtained from experiments with murine models of allergic airway and skin inflammation and offer an overview of studies focusing on miRNA discovery using profiling techniques and bioinformatic modeling of the network effect of multiple miRNAs. In conclusion, we highlight the importance of research into miRNA function in allergy and asthma to improve our knowledge of the molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of this heterogeneous group of diseases.
Keywords: allergic disease; asthma; experimental models; microRNA; pollution.
© 2020 The Authors. Allergy published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Weidner has nothing to disclose. Dr Bartel reports grants and personal fees from Bencard Allergie GmbH, outside the submitted work. Dr Kilic has nothing to disclose. Dr Zissler has nothing to disclose. Dr Renz has nothing to disclose. Dr Schwarze reports personal fees from MYLAN, personal fees from F2F events, outside the submitted work; and Industry support to educational activities of the Scottish Allergy and Respiratory Academy and of the Children's and Young people's Allergy Network Scotland. Industry support to EAACI, he is EAACI Secretary General 2019‐2021. Prof. Schmidt‐Weber reports grants from DFG, grants from BMBF, grants from EIT Health, and grants from German Center of lung research, outside the submitted work. Dr Maes reports grants from Ghent University, grants from Fund for Scientific Research in Flanders, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline, outside the submitted work; and is shareholder from Oryzon Genomics and Mendelion Lifesciences SL. Dr Rebane has nothing to disclose. Dr Krauss‐Etschmann has nothing to disclose. Dr Rådinger reports grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

