Onodera's prognostic nutritional index is a strong prognostic indicator for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after initial hepatectomy, especially patients with preserved liver function
- PMID: 33129309
- PMCID: PMC7603728
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-020-00917-2
Onodera's prognostic nutritional index is a strong prognostic indicator for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after initial hepatectomy, especially patients with preserved liver function
Abstract
Background: Several inflammation-based scores are used to assess the surgical outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim of the present study was to elucidate the prognostic value of the prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in HCC patients who underwent hepatectomy with special attention to preoperative liver functional reserve.
Methods: Preoperative demographic and tumor-related factors were analyzed in 189 patients with HCC undergoing initial hepatectomy from August 2005 to May 2016 to identify significant prognostic factors.
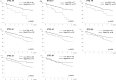
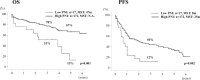
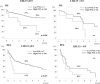
Results: Multivariate analysis for overall survival (OS) revealed that female sex (p = 0.005), tumor size (p < 0.001) and PNI (p = 0.001) were independent prognostic factors. Compared to the High PNI group (PNI ≥ 37, n = 172), the Low PNI group (PNI < 37, n = 17) had impaired liver function and significantly poorer OS (13% vs. 67% in 5-year OS, p = 0.001) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) (8 vs. 25 months in median PFS time, p = 0.002). In the subgroup of patients with a preserved liver function of LHL15 ≥ 0.9, PNI was also independent prognostic factor, and OS (21% vs. 70% in 5-year OS, p = 0.008) and RFS (8 vs. 28 months in median PFS time, p = 0.018) were significantly poorer in the Low PNI group than the High PNI group.
Conclusions: PNI was an independent prognostic factor for HCC patients who underwent hepatectomy. Patients with PNI lower than 37 were at high risk for early recurrence and poor patient survival, especially in the patients with preserved liver function of LHL ≥ 0.9.
Keywords: ALBI grade; GPS; Hepatectomy; Hepatocellular carcinoma; LHL15; Liver functional reserve; NLR; PLR; PNI; Technetium-99 m-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-galactosyl-human serum albumin (99mTc-GSA) liver scintigraphy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Smith RA, Bosonnet L, Ghaneh P, Sutton R, Evans J, Healey P, et al. The platelet-lymphocyte ratio improves the predictive value of serum CA19-9 levels in determining patient selection for staging laparoscopy in suspected periampullary cancer. Surgery. 2008;143:658–666. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.12.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Onodera T, Goseki N, Kosaki G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1984;85:1001–1005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

