Cyclic imine toxins survey in coastal european shellfish samples: Bioaccumulation and mode of action of 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G. first report of portimine-A bioaccumulation
- PMID: 33129465
- PMCID: PMC7657664
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101887
Cyclic imine toxins survey in coastal european shellfish samples: Bioaccumulation and mode of action of 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G. first report of portimine-A bioaccumulation
Abstract
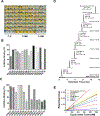
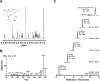
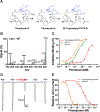
Cyclic imine toxins exhibit fast acting neurotoxicity and lethality by respiratory arrest in mice explained by their potent antagonistic activity against muscular nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. We performed a survey of gymnodimine-A, 13-desmethyl spirolide-C, 13,19-didesmethyl spirolide-C, 20-methyl spirolide-G, pinnatoxin-A, pinnatoxin-G, portimine-A and 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G in 36 shellfish samples collected in coastal areas of 8 European countries using a microplate receptor binding assay and UPLC-MS/MS for toxin identification and quantification. The major toxins found in these samples were pinnatoxin-G, 20-methyl spirolide-G, 13-desmethyl spirolide-C, gymnodimine-A and portimine-A. Traces of 13,19-didesmethyl spirolide-C, pinnatoxin-A and 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G were also detected. The rapid death of mice was correlated with higher pinnatoxin-G concentrations in mussel digestive gland extracts injected intraperitoneally. Our survey included nontoxic control samples that were found to contain moderate to trace amounts of several cyclic imine toxins. Shellfish may bioaccumulate not only cyclic imine toxins but also a large number of acyl derivatives as a product of metabolic transformation of these neurotoxins. This is the first report in which portimine-A and 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G were detected in shellfish extracts from digestive glands of mussels collected in Ingril lagoon. The bioaccumulation of portimine-A is particularly of concern because it is cytotoxic and is able to induce apotosis. The mode of action of 28-O-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G was studied by receptor binding-assay and by two-electrode voltage clamp electrophysiology. The antagonistic behavior of the acylated pinnatoxin-G towards nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of muscle type is shown here for the first time. Since cyclic imine toxins are not regulated further monitoring of these emerging toxins is needed to improve evidence gathering of their occurrence in shellfish commercialized for human consumption in Europe given their potent antagonism against muscle and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
Keywords: 28-o-palmitoyl ester of pinnatoxin-G; Cyclic imine toxins; Microplate receptor-binding assay; Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; Pinnatoxin-G; Portimine-A; Two-electrode voltage clamp electrophysiology.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Aasen J, MacKinnon SL, Le Blanc P, Walter JA, Hovgaard P, Aune T, Quilliam MA 2005. Detection and identification of spirolides in Norwegian shellfish and plankton. Chem. Res. Toxicol 18(3), 509–515. - PubMed
-
- Aasen JAB, Hardstaff W, Aune T, Quilliam MA 2006. Discovery of fatty acid ester metabolites of spirolide toxins in mussels from Norway using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 20(10), 1531–1537. - PubMed
-
- Abadie E, Chiantella C, Crottier A, Rhodes L, Masseret E, Berteaux T, Laabir M. 2018. What are the main environmental factors driving the development of the neurotoxic dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum in a Mediterranean ecosystem (Ingril lagoon, France)? Harmful Algae 75, 75–86. - PubMed
-
- Alonso E, Otero P, Vale C, Alfonso A, Antelo A, Gimenez-Llort L, Chabaud L, Guillou C, Botana LM 2013. Benefit of 13-desmethyl Spirolide C treatment in triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer Disease: beta-amyloid and neuronal markers improvement. Curr. Alzheimer Res 10(3), 279–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

