The Role of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 in Modulating Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Inflammation, and Coronavirus Infection
- PMID: 33130103
- PMCID: PMC7836226
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.067
The Role of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 in Modulating Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Inflammation, and Coronavirus Infection
Abstract
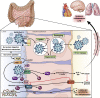
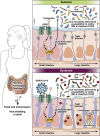
The role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 has expanded from regulating the renin angiotensin system to regulating intestinal amino acid homeostasis and the gut microbiome. Recently, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 was identified as a primary receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses 1 and 2 being expressed in multiple tissues including the luminal surface of the gut. In this brief perspective, we examine the role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 as the receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and the impact of coronavirus disease 19 infection on the gut microbiome and on the gut epithelium.
Keywords: ACE2; Gut Microbiota; SAR-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Vickers C., Hales P., Kaushik V. Hydrolysis of biologic peptides by human angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:14838–14843. - PubMed
-
- Kuba K., Imai Y., Penninger J.M. Multiple functions of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and is relevance in cardiovascular diseases. Circ J. 2013;77:301–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

