Residual SARS-CoV-2 RNA in nasal swabs of convalescent COVID-19 patients: Is prolonged quarantine always justified?
- PMID: 33130202
- PMCID: PMC7834568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.072
Residual SARS-CoV-2 RNA in nasal swabs of convalescent COVID-19 patients: Is prolonged quarantine always justified?
Abstract
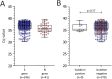
Real-time reverse transcription PCR is currently the most sensitive method to detect severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Defining whether a patient could be contagious or not contagious in the presence of residual SARS-CoV-2 RNA is of extreme importance in the context of public health. In this prospective multicenter study, virus isolation was prospectively attempted in 387 nasal swabs from clinically recovered patients showing low viral load (quantification cycle, Cq, value greater than 30). The median Cq value was 36.8 (range 30.0-39.4). Overall, a cytopathic effect was detected in nine samples, corresponding to a culture positivity rate of 2.3% (9/387). The results of this study help to dissect true virus replication and residual viral RNA detection in recovered patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cq value; Infectivity; Real-time reverse transcription PCR; SARS-CoV-2; Virus isolation.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Canters for Disease Control and Prevention . 2020. CDC’s diagnostic multiplex assay for Flu and COVID-19 at public health laboratories and supplies.https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/multiplex.html (Accessed 14 September 2020)
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 2020. CDC 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) real-time RT-PCR diagnostic panel.https://www.fda.gov/media/134922/download [Accessed 18 June 2020]
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous