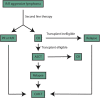
Clinical Perspective: Treatment of Aggressive B Cell Lymphomas with FDA-Approved CAR-T Cell Therapies
- PMID: 33130313
- PMCID: PMC7854294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.10.022
Clinical Perspective: Treatment of Aggressive B Cell Lymphomas with FDA-Approved CAR-T Cell Therapies
Abstract
Large B cell lymphoma (LBCL) is curable with standard chemo-immunotherapy in the majority of cases. However, patients with primary refractory or relapsed disease have historically had limited treatment options. Two gene-modified chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies have now been approved for these indications. The clinical decisions and management surrounding these gene-modified "living drugs" are nuanced and complex. In this article, we discuss the evolving evidence supporting the use of these CAR-T cells, including patient selection, screening procedures, special populations, bridging therapy, lymphodepletion, clinical management, relapse, and follow up.
Copyright © 2020 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest M.J.F. and M.V.M. have received sponsored research support from Kite Pharma and Novartis and are investigators and consultants on multiple industry-sponsored trials of CAR-T cells. M.V.M. holds equity in Century Therapeutics and TCR2.
Figures
References
-
- Union for International Camcer Control . 2014. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. 2014 Review of Cancer Medicines on the WHO List of Essential medicines.https://www.who.int/selection_medicines/committees/expert/20/application...
-
- Van Den Neste E., Schmitz N., Mounier N., Gill D., Linch D., Trneny M., Bouadballah R., Radford J., Bargetzi M., Ribrag V. Outcomes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients relapsing after autologous stem cell transplantation: an analysis of patients included in the CORAL study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52:216–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources