The potential of using blood circular RNA as liquid biopsy biomarker for human diseases
- PMID: 33131025
- PMCID: PMC8674396
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-020-00799-3
The potential of using blood circular RNA as liquid biopsy biomarker for human diseases
Abstract
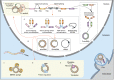
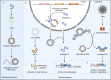
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a novel class of single-stranded RNAs with a closed loop structure. The majority of circRNAs are formed by a back-splicing process in pre-mRNA splicing. Their expression is dynamically regulated and shows spatiotemporal patterns among cell types, tissues and developmental stages. CircRNAs have important biological functions in many physiological processes, and their aberrant expression is implicated in many human diseases. Due to their high stability, circRNAs are becoming promising biomarkers in many human diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases and human cancers. In this review, we focus on the translational potential of using human blood circRNAs as liquid biopsy biomarkers for human diseases. We highlight their abundant expression, essential biological functions and significant correlations to human diseases in various components of peripheral blood, including whole blood, blood cells and extracellular vesicles. In addition, we summarize the current knowledge of blood circRNA biomarkers for disease diagnosis or prognosis.
Keywords: human diseases; liquid biopsy; peripheral blood circular RNA; translational biomarkers.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Guoxia Wen, Tong Zhou and Wanjun Gu declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Circular RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2020 Aug;13(4):572-583. doi: 10.1007/s12265-019-09912-2. Epub 2020 May 12. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32399680 Review.
-
Circular RNA landscape in extracellular vesicles from human biofluids.Genome Med. 2024 Oct 31;16(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01400-w. Genome Med. 2024. PMID: 39482783 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in body fluids as cancer biomarkers: the new frontier of liquid biopsies.Mol Cancer. 2021 Jan 11;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01298-z. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33430880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs: Promising Biomarkers for Human Diseases.EBioMedicine. 2018 Aug;34:267-274. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.036. Epub 2018 Aug 2. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30078734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs are a novel type of non-coding RNAs in ROS regulation, cardiovascular metabolic inflammations and cancers.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Apr;220:107715. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107715. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33141028 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress of Circular RNA in Gastrointestinal Tumors.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 15;11:665246. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.665246. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33937077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyses of circRNA and mRNA Profiles in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:738760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.738760. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003060 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Sex Differences in ncRNAs Expression and Function in Pregnancy and Related Complications.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 20;9(11):1509. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111509. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in gastric cancer: role of exosomal lncRNA and microRNA as diagnostic and therapeutic targets.Front Physiol. 2023 Aug 16;14:1158839. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1158839. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37664422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Emerging roles of circular RNAs in the tumor: functions and potential applications-volume II.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Mar 21;12:1339274. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1339274. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38577505 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aktaş T, Ilık İ, Maticzka D, Bhardwaj V, Rodrigues C, Mittler G, Manke T, Backofen R, Akhtar A. DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome. Nature. 2017;544:115–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

