Preoperative computerized tomography screening for COVID-19 pneumonia in asymptomatic patients: experiences from two centers
- PMID: 33131031
- PMCID: PMC7603412
- DOI: 10.1007/s11604-020-01061-w
Preoperative computerized tomography screening for COVID-19 pneumonia in asymptomatic patients: experiences from two centers
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this retrospective study is to evaluate the preoperative screening performance of chest CT (computerized tomography) examination to detect COVID-19 positive individuals.
Materials and methods: In this retrospective study 218 adult patients who had preoperative chest CT and RT-PCR were enrolled. CT imaging results, which have been reported according to the Radiological Society of North America expert consensus on COVID-19, were collected from the picture archiving and communicating system. Demographic data, planned surgeries, and postoperative outcomes were collected from the electronic patient records.
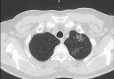
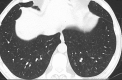
Results: One patient (0.5%) showed typical CT features for COVID-19 pneumonia; 12 patients (5.5%) were reported as indeterminate, and eight (3.7%) were reported as atypical for COVID-19 pneumonia. Only one of the three patients with positive RT-PCR had abnormalities on CT. When RT-PCR tests were taken as reference, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of chest CT in showing COVID-19 infection in asymptomatic patients were 33.3%, 90.7%, and 90.0%, respectively.
Conclusion: Chest CT screening for COVID-19 has a very low yield in asymptomatic preoperative patients and shows false-positive findings in 9.2% of cases, potentially leading to unnecessary postponing of the surgery.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest CT; Screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Timeline—COVID-19. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-04-2020-who-timeline---COVID-19. Accessed 7 Jul 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Available at: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed July 7, 2020.
-
- Kokkinakis I, Selby K, Favrat B, et al. Performance du frottis nasopharyngé-PCR pour le diagnostic du Covid-19—recommandations pratiques sur la base des premières données scientifiques [Covid-19 diagnosis: clinical recommendations and performance of nasopharyngeal swab-PCR] Rev Med Suisse. 2020;16(689):699–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

