Metabolic profiling reveals dysregulated lipid metabolism and potential biomarkers associated with the development and progression of Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS)
- PMID: 33131090
- PMCID: PMC7756608
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202001880R
Metabolic profiling reveals dysregulated lipid metabolism and potential biomarkers associated with the development and progression of Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS)
Abstract
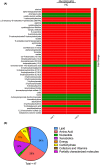
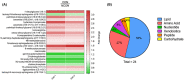
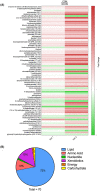
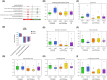
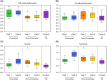
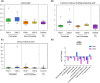
Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) is a neurodegenerative disorder associated with the FMR1 premutation. It is currently unknown when, and if, individual premutation carriers will develop FXTAS. Thus, with the aim of identifying biomarkers for early diagnosis, development, and progression of FXTAS, we performed global metabolomic profiling of premutation carriers (PM) who, as part of an ongoing longitudinal study, emerged into two distinct categories: those who developed symptoms of FXTAS (converters, CON) at subsequent visits and those who did not (non-converters, NCON) and we compared to age-matched healthy controls (HC). We assessed CGG repeat allele size by Southern Blot and PCR analysis. Metabolomic profile was obtained by ultra-performance liquid chromatography, accurate mass spectrometer, and an Orbitrap mass analyzer. In this study we found 47 metabolites were significantly dysregulated between HC and the premutation groups (PM). Importantly, we identified 24 metabolites that showed significant changes in expression in the CON as compared to the NCON both at V1 and V2, and 70 metabolites in CON as compared to NCON but only at V2. These findings suggest the potential role of the identified metabolites as biomarkers for early diagnosis and for FXTAS disease progression, respectively. Interestingly, the majority of the identified metabolites were lipids, followed by amino acids. To our knowledge, this the first report of longitudinal metabolic profiling and identification of unique biomarkers of FXTAS. The lipid metabolism and specifically the sub pathways involved in mitochondrial bioenergetics, as observed in other neurodegenerative disorders, are significantly altered in FXTAS.
Keywords: FMR1; fatty acids; fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome; metabolomic; molecular biomarkers.
© 2020 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Zafarullah, G. Palczewski and S.M. Rivera: No disclosures to report.
D.R. Hessl: Has received the funding from Novartis, Roche, Seaside Therapeutics LLC and Marinus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for designing Fragile X clinical Trials.
F. Tassone: Has received the funding from Azrieli Foundation, Zynerba and Asuragen, Inc. for studies in Fragile X syndrome.
Figures

References
-
- Heemels M‐T. Neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2016;539:179. - PubMed
-
- Hagerman RJ, Hagerman P. Fragile X‐associated tremor/ataxia syndrome — features, mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:403‐412. - PubMed
-
- Hagerman RJ, Berry‐Kravis E, Hazlett HC, et al. Fragile X syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17065. - PubMed
-
- Jacquemont S. Penetrance of the Fragile X‐associated tremor/ataxia syndrome in a premutation carrier population. JAMA. 2004;291:460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

