Prognostic role of vitamin D receptor in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33131491
- PMCID: PMC7603743
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07559-w
Prognostic role of vitamin D receptor in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: A higher vitamin D intake improves the prognosis of early stage breast cancer (BC) patients. We hypothesized that vitamin D intake should refer to vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression. In order to prove this hypothesis, we first intend to evaluate the correlation between VDR expression and prognosis of BC patients using meta-analysis.
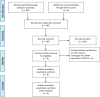
Methods: Literatures from PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library (last update by May 20, 2020) were retrieved to find studies assessing the prognostic role of VDR in BC. The hazard ratios (HRs) for patients' survival were extracted for pooled analyses. Subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis and meta-regression were performed to explore the sources of heterogeneity.
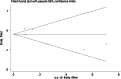
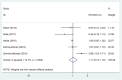
Results: Seven articles containing eight studies with 2503 patients were enrolled. The results from the pooled analyses showed that the VDR expression generally had no relationship with BC patients' overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and progression-free survival (PFS) (P > 0.05). Because only the number of studies exploring the relationship between VDR expression and OS is greater than five and there is heterogeneity, we explored the sources of heterogeneity of these studies. Subgroup analyses showed that the VDR expression in the nucleus had no relationship with OS, but high total VDR expression in the nucleus and cytoplasm was related to a better OS (pooled HR = 0.41; 95% CI = 0.18-0.95; P = 0.038). In addition, in subgroup of studies using cut-off values other than 'immunoreactive score (IRS)>5' and 'IRS > 25', high VDR expression was associated with a better OS (pooled HR = 0.47; 95% CI = 0.30-0.74; P = 0.001). Sensitivity analysis showed that the result pattern was not obviously affected by any single study. Meta-regression showed that the source of heterogeneity was not country (P = 0.657), pathological type (P = 0.614), molecular type (P = 0.423), staining location (P = 0.481), or cut-off value (P = 0.509).
Conclusions: The protein expression level of VDR in entire BC cells evaluated by immunohistochemistry is related to the OS of BC patients. It is expected that a more individualized vitamin D intake and a more accurate prognosis assessment can be recommended for BC patients based on the VDR expression. Of course, more preclinical and clinical studies are needed.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Meta-analysis; Prognosis; Vitamin D receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The association between vitamin D receptor expression and prolonged overall survival in breast cancer.J Histochem Cytochem. 2012 Feb;60(2):121-9. doi: 10.1369/0022155411429155. Epub 2011 Nov 21. J Histochem Cytochem. 2012. PMID: 22108646 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Expression of Vitamin D Receptor and Breast Cancer Histopathological Characteristics and Prognosis.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 1;23(1):97-103. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0075. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27407090 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of VDR in Bone Metastasis and Prognosis of Patients with Breast Cancer and Expression Correlation between Vitamin D Receptor and Hairless Protein.Oncol Res Treat. 2022;45(4):166-177. doi: 10.1159/000521078. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Oncol Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 34818655
-
High Ki-67 Immunohistochemical Reactivity Correlates With Poor Prognosis in Bladder Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis with 13,053 Patients Involved.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(15):e3337. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003337. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27082587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognosis difference between HER2-low and HER2-zero breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer. 2023 Nov;30(6):965-975. doi: 10.1007/s12282-023-01487-w. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37470943
Cited by
-
Vitamin D Receptor Expression and its Clinical Significance in Papillary Thyroid Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221089933. doi: 10.1177/15330338221089933. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35379049 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Update.JBMR Plus. 2021 Dec 10;5(12):e10582. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10582. eCollection 2021 Dec. JBMR Plus. 2021. PMID: 34950835 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D receptor is associated with prognostic characteristics of breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy-an observational study.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 1;14:1458124. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1458124. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39411136 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis in Iranian patients.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Jul 11;80:104162. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104162. eCollection 2022 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36045810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Diagnosis Vitamin D Supplement Use and Survival among Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 19;14(16):3418. doi: 10.3390/nu14163418. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Pineros M, Znaor A, Bray F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–1953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

