Evaluation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex in patients with chronic otitis media
- PMID: 33132091
- PMCID: PMC9483944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.09.006
Evaluation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex in patients with chronic otitis media
Abstract
Introduction: In recent years, scientific evidence has shown that chronic otitis media may cause balance and vestibular dysfunction.
Objective: To compare the results of the video head impulse test (gain and symmetry of the vestibulo-ocular reflex and presence of covert and overt saccades) in patients with chronic otitis media and controls.
Methods: Cross-sectional study of patients with chronic otitis media (study group), aged between 18 and 60 years. The patients in the study group were further divided according to the chronic otitis media type as (1) non-suppurative, (2) suppurative, and (3) cholesteatomatous. For the comparative analysis, we selected volunteers with no history of ear and vestibular diseases (control group), who met the same inclusion and exclusion criteria as the study group. Patients in both groups underwent a video head impulse test.
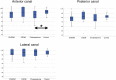
Results: The study group consisted of 96 volunteers, and the control group of 61 individuals. The prevalence of vestibular symptoms was 66% in the study group and 3.2% in the control group (p < 0.001). The results show a higher prevalence of changes in the vestibulo-ocular reflex gain (22.9%) and corrective saccades (12.6%) in the chronic otitis media group compared to the control group (p < 0.001). Despite the higher prevalence of changes in gain, the average vestibulo-ocular reflex gains in the chronic otitis media groups were within the pre-defined values of normality; however, the mean vestibulo-ocular reflex gain in the anterior semicircular canal was statistically worse in the cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media group compared to controls (p < 0.001). Regarding the corrective saccades, the prevalence of saccades was statistically higher in the suppurative and cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media subgroups compared to the non-suppurative and control groups (p = 0.004).
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that chronic otitis media is associated with a higher prevalence of vestibular symptoms and also a higher prevalence of changes in gain and corrective saccades when compared to controls.
Keywords: Head impulse test; Otitis media; Semicircular canals; Vestibular function tests; Vestibulo-ocular reflex.
Copyright © 2020 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Using the Video Head Impulse Test in Patients with Unilateral Chronic Otitis Media.Audiol Neurootol. 2024;29(5):351-356. doi: 10.1159/000538254. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Audiol Neurootol. 2024. PMID: 38452739
-
Evaluation of postural stability and vestibulo-ocular reflex in adults with chronic suppurative otitis media.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Feb;280(2):897-905. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07687-y. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36303036 Free PMC article.
-
The Conventional Head Impulse Test Versus the Suppression Head Impulse Test: A Clinical Comparative Study.J Int Adv Otol. 2023 Jan;19(1):41-44. doi: 10.5152/iao.2023.22860. J Int Adv Otol. 2023. PMID: 36718035 Free PMC article.
-
Video head impulse test: a review of the literature.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1215-1222. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4157-4. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27328962 Review.
-
Impulsive testing of semicircular-canal function using video-oculography.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 May;1164:486-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03730.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19645955 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Lateral Semicircular Canal Dysfunction in Chronic Otitis Media Patients using Air Caloric Test and Video Head Impulse Test.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Feb;77(2):832-836. doi: 10.1007/s12070-024-05264-9. Epub 2024 Dec 22. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40070758
-
Long-Term Impact of Recurrent Acute Otitis Media on Balance and Vestibular Function in Children.Brain Sci. 2024 Dec 12;14(12):1246. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14121246. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39766445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cordeiro F.P., Monsanto R.C., Kasemodel A.L.P., Gondra L.A., Penido N.O. Extended high-frequency hearing loss following the first episode of otitis media. Laryngoscope. 2018;128:2879–2884. - PubMed
-
- Monsanto R.C., Kasemodel A.L.P., Tomaz A., Paparella M.M., Penido N.O. Current evidence of peripheral vestibular symptoms secondary to otitis media. Ann Med. 2018;50:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Organization W.H. World Health Organization; 2018. Addressing the rising prevalence of hearing loss [Internet] https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/260336 [cited 2020 Mar 31]. Available from:
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

