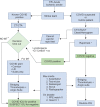
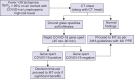
Practice Implications for Acute Ischemic Stroke during the COVID-19 Pandemic for the Indian Scenario: Realistic and Achievable Recommendations by the Society of Neurocritical Care (SNCC), India
- PMID: 33132556
- PMCID: PMC7584840
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23511
Practice Implications for Acute Ischemic Stroke during the COVID-19 Pandemic for the Indian Scenario: Realistic and Achievable Recommendations by the Society of Neurocritical Care (SNCC), India
Abstract
COVID-19 disease caused by the SARS coronavirus has caused significant morbidity and mortality around the world ever since it was first declared as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020. Acute neurological manifestations of this disease have also started emerging and being recognized around the world and acute ischemic stroke (AIS) or thrombotic stroke is becoming one of the major neurological illnesses related to COVID-19. The management of AIS is time-critical and major advances in its management over the recent years, such as bridging thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy (MT), are multidisciplinary activities requiring robust coordination and management in the acute setting. All these advances are severely challenged in the COVID-19 pandemic where severe pressures exist on the clinical resources and logistics required to deliver an effective stroke service. This is further compromised by legal and preventive measures during this pandemic like local lockdowns. Reporting of minor or initial symptoms has also been compromised due to the fear of approaching healthcare settings which are perceived as high-risk zones to catch the infection. The purpose of this document is to highlight these challenges and provide a guiding framework for the management of AIS under three principles: (a) Delivering an effective service, (b) Preventing infections within the healthcare setting, and (c) Optimizing resource utilization. How to cite this article: Kakkar G, Zirpe KG, Sapra H, Dixit S, Chugh C, Nagaiyan S, et al. Practice Implications for Acute Ischemic Stroke during the COVID-19 Pandemic for the Indian Scenario: Realistic and Achievable Recommendations by the Society of Neurocritical Care (SNCC), India. Indian J Crit Care Med 2020;24(9):757-762.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; COVID stroke pathway; COVID-19; Healthcare staff protection; Hyperacute stroke service; Mechanical thrombectomy; Neurocritical care; Thrombolysis; Thrombotic stroke.
Copyright © 2020; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Similar articles
-
Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine Position Statement for Central Venous Catheterization and Management 2020.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020 Jan;24(Suppl 1):S6-S30. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-G23183. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32205954 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Neurological Manifestations in COVID-19.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020 Oct;24(10):975-980. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23592. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 33281325 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) in COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review.Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg. 2021;57(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s41983-021-00321-4. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34093003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of acute ischemic stroke in patients with COVID-19 infection: Report of an international panel.Int J Stroke. 2020 Jul;15(5):540-554. doi: 10.1177/1747493020923234. Epub 2020 May 3. Int J Stroke. 2020. PMID: 32362244
-
A full year of the COVID-19 pandemic with two infection waves and its impact on ischemic stroke patient care in Germany.Eur J Neurol. 2022 Jan;29(1):105-113. doi: 10.1111/ene.15057. Epub 2021 Aug 22. Eur J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34370900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
International alliance and AGREE-ment of 71 clinical practice guidelines on the management of critical care patients with COVID-19: a living systematic review.J Clin Epidemiol. 2022 Feb;142:333-370. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.11.010. Epub 2021 Nov 14. J Clin Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 34785346 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of standardized nursing cooperation on intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in acute ischemic stroke.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):11925-11931. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34786123 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Vision, Aphasia, Neglect Assessment in Predicting Emergent Large Vessel Occlusion in Patients Presenting with a Cerebrovascular Accident to the Emergency Department.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2023 Jul;27(7):475-481. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24485. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 37502295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Y, Wang M, Zhou Y, et al. Acute cerebrovascular disease following COVID-19: a single centre, retrospective, observational study (3/3/2020). SSRN Elect J. 2020. https://ssrn.com/abstract1/43550025. http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3550025. https://ssrn.com/abstract1/43550025http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3550025 DOI: or. (accessed 17 April 2020) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zunt J. Invited commentary: neurology during the COVID-19 pandemic: lessons learned at the initial U.S. epicenter. Neurology. 2020. blogs.neurology.org. blogs.neurology.org Available at: (accessed 10 April 2020)
-
- Mao L, Wang M, Chen S, He Q, Chang J, Hong C, et al. Neurological manifestations of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective case series study. medRxiv. 2020. DOI: (accessed 17 April 2020) - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous