Chronic unpredictable stress-induced inflammation and quantitative analysis of neurons of distinct brain regions in Wistar rat model of comorbid depression
- PMID: 33132599
- PMCID: PMC7566234
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.1870-1874
Chronic unpredictable stress-induced inflammation and quantitative analysis of neurons of distinct brain regions in Wistar rat model of comorbid depression
Abstract
Background and aim: Depression and anxiety are the most prominent neuropsychiatric disease and have been considered as the most burdensome diseases of society. The hippocampus and prefrontal cortex have a prominent role in stress-induced neurological disorders. Chronic unpredictable stress exposed rats are a perfect model in understanding comorbid depression and anxiety disorders. The inflammatory response occurring in the body has been linked to C-reactive protein (CRP) in many diseased conditions. The present research primarily focus on the possible correlation of Cortisol, CRP level and neuronal assay in different regions of hippocampus, dentate gyrus (DG), and prefrontal cortex.
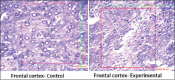
Materials and methods: The control group of rats (n=6) was not exposed to any stress. Whereas, the experimental stress group (n=6) of rats was exposed to various stressors for 15 days. After the experimentation procedures, the blood samples were collected and brain dissection was done. The neurons in the prefrontal cortex, the DG along with various hippocampal regions was counted. Statistical analysis was performed using student's t-test and p<0.05 was expressed as statistically significant.
Results: Animals exposed to chronic unpredictable stressors showed a significant (p<0.0001) decrease in the neuronal count in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. A significant rise in the serum cortisol (p<0.0001) and CRP (p<0.001) was witnessed in the stressed group.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that chronic unpredictable stress exposure has affected neurogenesis in prefrontal cortex and hippocampal regions. Decreased neurogenesis was well in coordinance with the increase in cortisol and CRP. The chronic unpredictable stress-induced inflammatory response correlated to various brain regions might provoke insights into a variety of new drugs targeting neurogenesis.
Keywords: C reactive protein; anxiety; cortisol; depression; neuronal count; rat model; stress.
Copyright: © Blossom, et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynamic changes of behaviors, dentate gyrus neurogenesis and hippocampal miR-124 expression in rats with depression induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jun;15(6):1150-1159. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.270414. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31823896 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting neurogenesis in hippocampal dentate gyrus of chronic unpredictable stress-induced depressive-like rats with paeoniflorin.J Integr Neurosci. 2019 Mar 30;18(1):43-49. doi: 10.31083/j.jin.2019.01.116. J Integr Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31091847
-
Evaluation of biomarkers of stress in chronic stress-exposed comorbid depression model Wistar rats.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 30;30(5). doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2018-0215. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31469653
-
Anxiolytic effects of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors agonist oxotremorine in chronically stressed rats and related changes in BDNF and FGF2 levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Feb;234(4):559-573. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4498-0. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 27957715
-
Rodent models of social stress and neuronal plasticity: Relevance to depressive-like disorders.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Sep 2;369:111900. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111900. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31022420 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective role of virgin coconut oil on potent biochemical biomarkers in Wistar rat model of comorbid depression.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2024 Jun 12;11(2):449-454. doi: 10.5455/javar.2024.k794. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2024. PMID: 39101102 Free PMC article.
-
The Neurobiological Links between Stress and Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review of Research to Date.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 23;23(17):9519. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179519. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36076917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective role of cod liver oil on hippocampal oxidative damage and neuronal count in Wistar rat model of comorbid depression.Open Vet J. 2023 Apr;13(4):473-480. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i4.9. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Open Vet J. 2023. PMID: 37251260 Free PMC article.
-
Implicating neuroinflammation in hippocampus, prefrontal cortex and amygdala with cognitive deficit: a narrative review.3 Biotech. 2025 Sep;15(9):320. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04468-2. Epub 2025 Aug 30. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40893157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Stress on Brain Morphology: Insights into Structural Biomarkers of Stress-related Disorders.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(5):935-962. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230703091435. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37403395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nayanatara A.K, Nagaraja H.S, Ramaswamy C, Bhagyalakshmi K, Bhat M.R, Gowda K.M.D, Mantur V.S. Effect of chronic unpredictable stressors on some selected lipid parameters and biochemical parameters in wistar rats. J. Chin. Clin. Med. 2009;4(21):92–97.
-
- Nayanatara A.K, Gokul M, Kini R.D, Bhagyalakshmi K, Anupama N, Shetty S.B, Vinodini N.A, Bhat R, Pai S.R, Kaupu R. Effect of chronic unpredictable stressors on reproductive parameters in male wistar rats:Role of ascorbic acid. Int J Biol . Med. Res. 2014;5(4):4644–4647.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
