Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolated from ovine respiratory infection: A study from Karnataka, Southern India
- PMID: 33132610
- PMCID: PMC7566252
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.1947-1954
Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolated from ovine respiratory infection: A study from Karnataka, Southern India
Abstract
Background and aim: Respiratory infection due to Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida are responsible for huge economic losses in livestock sector globally and it is poorly understood in ovine population. The study aimed to investigate and characterize M. haemolytica and P. multocida from infected and healthy sheep to rule out the involvement of these bacteria in the disease.
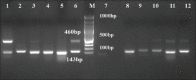
Materials and methods: A total of 374 healthy and infected sheep samples were processed for isolation, direct detection by multiplex PCR (mPCR), and antibiotic susceptibility testing by phenotypic and genotypic methods.
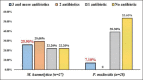
Results: Overall, 55 Pasteurella isolates (27 [7.2%] M. haemolytica and 28 [7.4%] P. multocida) were recovered and identified by bacteriological tests and species-specific PCR assays. Significant correlation between the detection of M. haemolytica (66.6%) with disease condition and P. multocida (19.1%) exclusively from infected sheep was recorded by mPCR. In vitro antibiotic susceptibility testing of 55 isolates revealed higher multidrug resistance in M. haemolytica (25.9%) than P. multocida (7.1%) isolates. Descending resistance towards penicillin (63.6%), oxytetracycline (23.6%), streptomycin (14.5%), and gentamicin (12.7%) and absolute sensitivity towards chloramphenicol were observed in both the pathogens. The antibiotic resistance genes such as strA (32.7%) and sul2 (32.7%) associated with streptomycin and sulfonamide resistance, respectively, were detected in the isolates.
Conclusion: The study revealed the significant involvement of M. haemolytica together with P. multocida in ovine respiratory infection and is probably responsible for frequent disease outbreaks even after vaccination against hemorrhagic septicemia in sheep population of Karnataka, southern province of India.
Keywords: Mannheima haemolytica; Pasteurella multocida; antimicrobial susceptibility; isolation; multiplex PCR.
Copyright: © Sahay, et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles among commensal Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolated from apparently healthy sheep processed in California: Results from a cross-sectional pilot study.Prev Vet Med. 2024 Dec;233:106360. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2024.106360. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Prev Vet Med. 2024. PMID: 39461021
-
Identification of serotypes of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida from pneumonic cases of sheep and goats and their antimicrobial sensitivity profiles in Borana and Arsi zones, Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 2;13(1):9008. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36026-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37268660 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Molecular Detection of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida from Clinically Pneumonic Pasteurellosis Cases of Bonga Sheep Breed and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Tests in Selected Areas of Southwest Ethiopian Peoples Regional State, Ethiopia.Vet Med (Auckl). 2023 Dec 27;14:233-244. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S435932. eCollection 2023. Vet Med (Auckl). 2023. PMID: 38162823 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and identification of caprine pasteurellosis in pneumonic goats in Bangladesh.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2023 Sep 30;10(3):538-544. doi: 10.5455/javar.2023.j707. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2023. PMID: 37969786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogens of Pasteurella.Vet Microbiol. 1993 Nov;37(3-4):353-68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(93)90034-5. Vet Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8116191 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation of the various serotypes of Mannheimia haemolytica and preparation of the first vaccine candidate in Iran.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Nov;49(11):10367-10375. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07890-4. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36097127
-
Sero-Prevalence of Hemorrhagic Septicaemia in Cattle and Buffalo Population of Indian States Karnataka and Gujarat.Vet Sci. 2024 Aug 22;11(8):386. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11080386. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39195840 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms, gene expression and evaluation of immunological, antioxidant, and pathological parameters associated with bacterial pneumonia in Barki sheep.Ir Vet J. 2025 Apr 12;78(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13620-025-00296-1. Ir Vet J. 2025. PMID: 40221769 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Molecular Detection of Pasteurellosis from Pneumonic Sheep in Selected Areas of Amhara Region, Ethiopia: An Implication for Designing Effective Ovine Pasteurellosis Vaccine.Vet Med (Auckl). 2022 Apr 24;13:75-83. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S365267. eCollection 2022. Vet Med (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35497709 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping Heterogeneous Population Structure of Mannheimia haemolytica Associated with Pneumonic Infection of Sheep in Southern State Karnataka, India.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Jun 11;81(8):219. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03740-7. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38862704
References
-
- Mohamed R.A, Addelsalam E.B. A review on pneumonic pasteurellosis (Respiratory mannheimiosis) with emphasis on pathogenesis, virulence mechanisms and predisposing factors. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2008;11(3):139–160.
-
- Lacasta D, Ferrer L.M, Ramos J.J, Gonzalez J.M, Heras D.L.M. Influence of climatic factors on the development of pneumonia in lambs. Small Rumin. Res. 2008;80(1-3):28–32.
-
- Dabo S.M, Taylor J.D, Confer A.W. Pasteurella multocida and bovine respiratory disease. Anim. Health. Res. Rev. 2007;8(2):129–150. - PubMed
-
- Sahay S, Shome R, Sankarasubramanian J, Vishnu U.S, Prajapati A, Natesan K, Shome B.R, Rahman H, Rajendhran J. Genome sequence analysis of the Indian strain Mannheimia haemolytica serotype A2 from ovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Ann. Microbiol. 2019;69(2):151–160.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
