Orthostatic retractor placement reduces operating time and post-operative inflammatory response during the learning curve of anterior approach THA
- PMID: 33132623
- PMCID: PMC7586062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2020.10.011
Orthostatic retractor placement reduces operating time and post-operative inflammatory response during the learning curve of anterior approach THA
Abstract
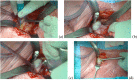
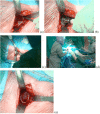
Introduction: Handheld retractor placement (HHRP) is prone to repetitive repositioning. This could lead to muscle damage especially during a procedure with a steep learning curve. In an attempt to minimize retractor repositioning during the learning curve of direct anterior approach (DAA) total hip arthroplasty (THA), we used a table mounted orthostatic retractor placement (ORP) device.
Purpose: To investigate whether ORP would reduce the extent of muscle damage, OR-time and post-operative inflammatory response.
Materials and methods: 29 Patients were operated by 2 surgeons who randomly used HHRP or ORP during their learning curve of DAA THA. There were 14 patients in a control group who were operated by an experienced surgeon. Blood levels of Creatine Kinase (CK), C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Hemoglobin (Hb), Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) were measured at 1 h pre- and 24 and 48 h post-operatively.
Results: The mean OR-time was 67 and 50 min in the HHRP and ORP cohort, respectively (p < 0,001). Post-operative CRP levels were significantly higher in the HHRP cohort at 24 h (HHRP 60.64 mg/L (25.20-143.20); ORP 34.67 mg/L (9.30-71.20)) (p = 0.003) and 48 h post-operatively (HHRP 154.54 mg/L (65.90-369.00); ORP 81.60 mg/L (21.30-219.40) (p = 0.004). The post-operative Hb-levels were significantly lower in the HHRP cohort at 24 h (HHRP 11.11 g/dL (9.10-12.30); ORP 11.37 g/dL (8.80-14.00)) (p = 0.0008) and 48 h (HHRP 10.86 g/dL (9.50-12.00); ORP 11.25 g/dL (8.60-14.10)) (p = 0.03). Post-operative ESR levels were significantly higher in the HHRP cohort 48 h post-op (HHRP 45.21 mm/h (14.00-83.00); ORP 23.73 mm/h (2.00-73.00)) (p = 0.004). No significant differences were found for the CK and LDH levels at any time postoperatively. There were no complications in any group.
Conclusion: The use of an orthostatic retractor placement device allows for reducing the OR-time, post-operative blood loss and post-operative inflammatory response during the learning curve of DAA THA.
Keywords: Direct anterior approach; Efficiency; Learning curve; Orthostatic retractor positioning reduces operating time and post-operative inflammatory response during the learning curve of anterior approach THA; Outcomes; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
First 100 total hip arthroplasties performed by a young surgeon using the direct anterior approach: learning curve and complications.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Feb;144(2):927-935. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-05077-5. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 37803086
-
Transitioning to the direct anterior approach in total hip arthroplasty. Is it a true muscle sparing approach when performed by a low volume hip replacement surgeon?Int Orthop. 2017 Nov;41(11):2245-2252. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3480-8. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Int Orthop. 2017. PMID: 28439629 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of traction table did not increase complications in total hip arthroplasty through direct anterior approach performed by novice surgeon.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020 Jan-Apr;28(2):2309499020923093. doi: 10.1177/2309499020923093. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020. PMID: 32583712
-
Direct anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty: indications, technique, and results.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014 Sep;22(9):595-603. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-22-09-595. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014. PMID: 25157041 Review.
-
Traction table versus standard table total hip arthroplasty through the direct anterior approach: a systematic review.Hip Int. 2020 Nov;30(6):662-672. doi: 10.1177/1120700019900987. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Hip Int. 2020. PMID: 31994425
Cited by
-
Perioperative Operating Room Efficiency Can Make Simultaneous Bilateral Total Hip Arthroplasty Cost-effective: A Proposal for a Value-sharing Model.Arthroplast Today. 2022 Nov 2;18:202-211.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2022.09.009. eCollection 2022 Dec. Arthroplast Today. 2022. PMID: 36561552 Free PMC article.
-
A novel nomogram for predicting non-infectious fever in patients following laparoscopic myomectomy.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27810. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78666-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mjaaland K.E., Kivle K., Svenningsen S., Pripp A.H., Nordsletten L. Comparison of markers for muscle damage, inflammation, and pain using minimally invasive direct anterior versus direct lateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(9):1305–1310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

