Role of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of oesophageal neoplasia: 2020 an endoscopic odyssey
- PMID: 33132634
- PMCID: PMC7579761
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5784
Role of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of oesophageal neoplasia: 2020 an endoscopic odyssey
Abstract
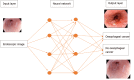
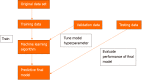
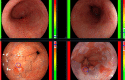
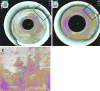
The past decade has seen significant advances in endoscopic imaging and optical enhancements to aid early diagnosis. There is still a treatment gap due to the underdiagnosis of lesions of the oesophagus. Computer aided diagnosis may play an important role in the coming years in providing an adjunct to endoscopists in the early detection and diagnosis of early oesophageal cancers, therefore curative endoscopic therapy can be offered. Research in this area of artificial intelligence is expanding and the future looks promising. In this review article we will review current advances in artificial intelligence in the oesophagus and future directions for development.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Barrett's oesophagus; Computer aided diagnosis; Deep learning; Oesophageal neoplasia; Squamous dysplasia.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Mohamed Hussein: No conflict of interest. Juana Gonzalez-Bueno Puyal: Employee at odin vision. Peter Mountney: Odin Vision employee. Laurence B lovat: Consultancy and minor share holder Odin Vision. Rehan Haidry: Educational grants to support research infrastructure from Medtronic ltd. Cook endoscopy (fellowship support), Pentax Europe, C2 therapeutics, Beamline diagnostic, Fractyl Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
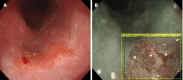
- Guo L, Xiao X, Wu C, Zeng X, Zhang Y, Du J, Bai S, Xie J, Zhang Z, Li Y, Wang X, Cheung O, Sharma M, Liu J, Hu B. Real-time automated diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using a deep learning model (with videos) Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:41–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

