In vitro and in vivo studies of nanoparticles of chitosan- Pandanus tectorius fruit extract as new alternative treatment for hypercholesterolemia via Scavenger Receptor Class B type 1 pathway
- PMID: 33132720
- PMCID: PMC7584805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.017
In vitro and in vivo studies of nanoparticles of chitosan- Pandanus tectorius fruit extract as new alternative treatment for hypercholesterolemia via Scavenger Receptor Class B type 1 pathway
Abstract
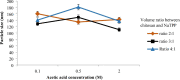
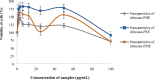
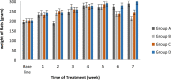
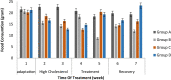
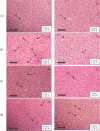
Pandanus tectorius fruit, a natural product rich in tangeretin and ethyl caffeate, has been reported to have potential as anti-hypercholesterolemia agent via Scavenger Receptor Class B type 1 (SR-B1) pathway. However, due to its semi-polar properties, P. tectorius extract exhibits poor solubility when used as a medical remedy. The extract's solubility can potentially be improved through a synthesis of nanoparticles of chitosan-P. tectorius fruit extract. This can also increase the extract's SR-B1 gene expression activity. To date, no studies of nanoparticles of chitosan-P. tectorius fruit extract and its pathway via SR-B1 have been published anywhere. In this study, cytotoxicity properties against HepG2 were explored by MTT. Then luciferase assay was used to detect their effectiveness in increasing SR-B1 activity. An in vivo study using Sprague dawley was carried out to observe the extract nanoparticles' effectiveness in reducing the cholesterol levels and the toxicity property in rat's liver. As the results showed, the extract nanoparticles had no cytotoxic activity against HepG2 cells and exhibited higher SR-B1 gene expression activity than the non-nanoparticle form. As the in vivo study proved, nanoparticle treatment can reduce the levels of TC (197%), LDL (360%), and TG (109%), as well as increase the level of HDL cholesterol by 150%, in comparison to those for the untreated high-cholesterol diet group. From the toxicity study, it was found that there was non-toxicity in the liver. It can be concluded that nanoparticles of chitosan-P. tectorius fruit extract successfully increased P. tectorius fruit extract's effectiveness in reducing hypercholesterolemia via SR-B1 pathway. Hence, it can be suggested that nanoparticles of chitosan-P. tectorius fruit extract is safe and suitable as an alternative treatment for controlling hypercholesterolemia via SR-B1 pathway.
Keywords: Chitosan nanoparticles; Hypercholesterolemia; Pandanus tectorius; SR-B1.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

