Development of novel pesticides in the 21st century
- PMID: 33132734
- PMCID: PMC7581488
- DOI: 10.1584/jpestics.D20-201
Development of novel pesticides in the 21st century
Abstract
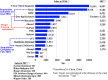
General trends and strategies for novel pesticides are summarized. Global pesticide sales and pesticide discovery research are also briefly reviewed. At least 105 chemical pesticides have been launched during the past decade or are under development: 43 fungicides, 34 insecticides/acaricides, 6 nematicides, 21 herbicides, and 1 herbicide safener. Most of them are safe to humans and environmentally friendly. The most developed fungicides are SDHI (succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors), DMI (demethylation inhibitors), QoI (quinone outside inhibitors), and QiI (quinone inside inhibitors). Due to the development of resistance to fungicides with existing modes of action, many fungicides possessing various novel modes of action have been launched or are under development. The trend of insecticide development is changing from organophosphorus, carbamate, and synthetic pyrethroids to nicotinic and diamide insecticides. During the past decade, compounds possessing a variety of novel modes of action have also been launched or are under development. Flupyradifurone and flupyrimin, exhibiting extremely low honeybee toxicity, have been developed and subjected to practical use. Herbicides possessing varied modes of action, such as acetolactate synthase, p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase, protoporphyrinogen oxidase, and very-long-chain fatty acid elongase inhibition, have been developed, but no herbicides possessing a novel mode action have commercialized in nearly 30 years. It is of interest that cyclopyrimorate, which was recently launched, and tetflupyrolimet, which is under development, have novel modes action: homogentisate solanesyltransferase (HST) and dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibition, respectively. The development of useful acaricides and nematicides is also progressing. Some natural product origin pesticides are getting attention.
Keywords: acaricide; fungicide; herbicide; insecticide; nematicide; novel pesticides.
© Pesticide Science Society of Japan 2020. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Figures


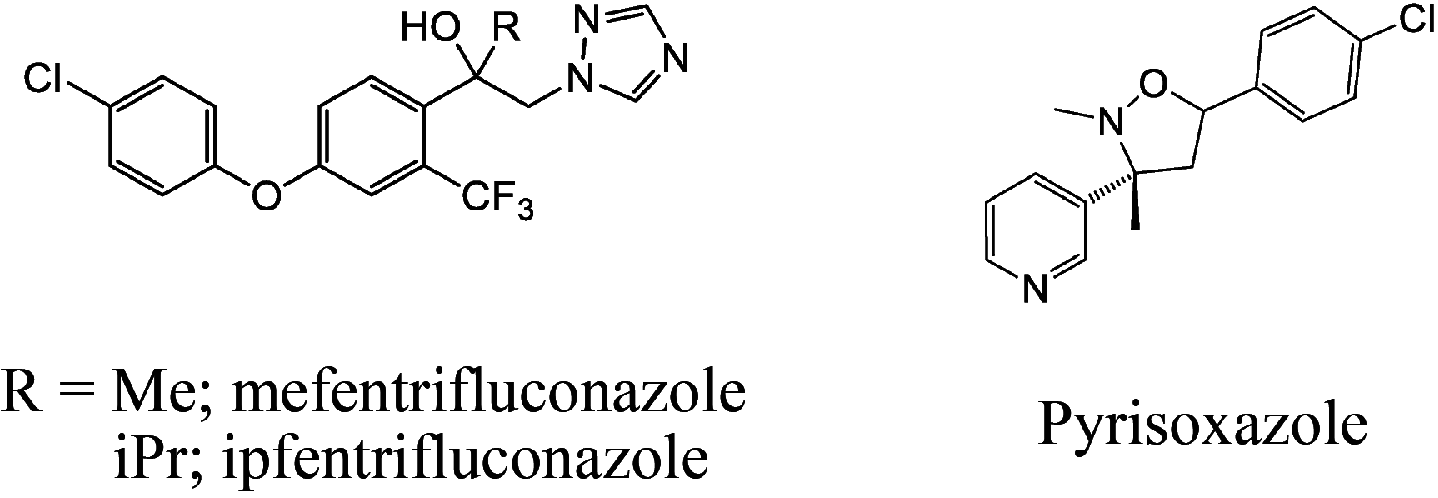




References
-
- 1) J. Unsworth, Y. Nakagawa, C. Harris and G. Kleter: The Battelle for a Sustainable Food Supply Chapter 2 (pp.13–84) in Sustainable Agrochemistry, A Compendium of Technologies, Ed. Silvio Vaz Jr., Springer Nature Switzerland, SBN978-3-030-1780-1, ISBN 978-3-030-17891-8 (e-book) (2019)
-
- 2) Trend in Pesticide Discovery Research—Development of Safer and Environmentally Friendly Pesticides—, N. Umetsu Supervised, CMC Publishing, 2018. (in Japanese).
-
- 3) N. Umetsu: Fine Chemical 47, 54–60 (2018) (in Japanese).
-
- 4) N. Umetsu: Fine Chemical 47, 53–60 (2018) (in Japanese).
-
- 5) N. Umetsu: Fine Chemical 48, 44–50 (2019) (in Japanese).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

