Serum Neurofilament Levels in Children With Febrile Seizures and in Controls
- PMID: 33132834
- PMCID: PMC7550525
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.579958
Serum Neurofilament Levels in Children With Febrile Seizures and in Controls
Abstract
Objective: Neuroaxonal damage is reflected by serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) values in a variety of acute and degenerative diseases of the brain. The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of febrile and epileptic seizures on sNfL, serum copeptin, and prolactin levels in children compared with children with febrile infections without convulsions.
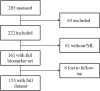
Methods: A prospective cross-sectional study was performed in children aging 6 months to 5 years presenting with fever (controls, n = 61), febrile seizures (FS, n = 78), or epileptic seizures (ES, n = 16) at our emergency department. sNfL, copeptin, and prolactin were measured within a few hours after the event in addition to standard clinical, neurophysiological, and laboratory assessment. All children were followed up for at least 1 year after presentation concerning recurrent seizures.
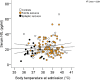
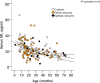
Results: Serum copeptin values were on average 4.1-fold higher in FS and 3.2-fold higher in ES compared with controls (both p < 0.01). Serum prolactin values were on average 1.3-fold higher in FS compared with controls ( p < 0.01) and without difference between ES and controls. There was no significant difference of mean sNfL values (95% CI) between all three groups, FS 21.7 pg/ml (19.6-23.9), ES 17.7 pg/ml (13.8-21.6), and controls 23.4 pg/ml (19.2-27.4). In multivariable analysis, age was the most important predictor of sNfL, followed by sex and C reactive protein. Neither the duration of seizures nor the time elapsed from seizure onset to blood sampling had an impact on sNfL. None of the three biomarkers were related to recurrent seizures.
Significance: Serum neurofilament light is not elevated during short recovery time after FS when compared with children presenting febrile infections without seizures. We demonstrate an age-dependent decrease of sNfL from early childhood until school age. In contrast to sNfL levels, copeptin and prolactin serum levels are elevated after FS.
Keywords: convulsion; epilepsy; neurofilament; neuronal biomarker; paroxysmal.
Copyright © 2020 Evers, Hügli, Fouzas, Kasser, Pohl, Stoecklin, Bernasconi, Kuhle and Wellmann.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum Neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels in children with and without neurologic diseases.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2023 Jul;45:9-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 May 6. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37236127
-
Copeptin as a serum biomarker of febrile seizures.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 20;10(4):e0124663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124663. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25894585 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neurofilament light (NfL) concentrations in patients with epilepsy with recurrent isolated seizures: Insights from a clinical cohort study.Seizure. 2024 Oct;121:91-94. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2024.08.006. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Seizure. 2024. PMID: 39137477
-
Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Predictive Biomarker for Ischemic Stroke Outcome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Jun;29(6):104813. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104813. Epub 2020 Apr 16. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32305278
-
The potential of serum neurofilament as biomarker for multiple sclerosis.Brain. 2021 Nov 29;144(10):2954-2963. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab241. Brain. 2021. PMID: 34180982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain and Tau Protein Levels in Cases with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Their Healthy Siblings and Healthy Controls.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2024 Aug 31;22(3):502-511. doi: 10.9758/cpn.23.1153. Epub 2024 May 23. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39069690 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the expression patterns of AVP, IGF-1, and TNF-α, APP, CD44, IFN-β IFN A β-6, α-syn, and NFL and CLU genes in generalized and focal seizures.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 19;10(14):e34912. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34912. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39149049 Free PMC article.
-
Review novel insights into the diagnostic and prognostic function of copeptin in daily clinical practice.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3755-3765. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08246-2. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. Retraction in: Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Aug;50(8):7143. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08615-x. PMID: 36662451 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Serum levels of neurofilament light chains in pediatric multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2023 Oct;270(10):4753-4762. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11841-9. Epub 2023 Jul 2. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37394516
-
Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain (NF-L) Is a Prognostic Biomarker for Cortical Damage Evolution but Not for Cognitive Impairment or Epileptogenesis Following Experimental TBI.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 2;23(23):15208. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315208. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burckhardt M. A., Wellmann M., Fouzas S., Lapaire O., Burkhardt T., Benzing J., et al. (2014). Sexual disparity of copeptin in healthy newborn infants. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99 E1750–E1753. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials