TRP Channels and Small GTPases Interplay in the Main Hallmarks of Metastatic Cancer
- PMID: 33132914
- PMCID: PMC7550629
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.581455
TRP Channels and Small GTPases Interplay in the Main Hallmarks of Metastatic Cancer
Abstract
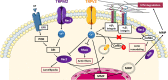
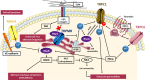
Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) cations channels, as key regulators of intracellular calcium homeostasis, play a central role in the essential hallmarks of cancer. Among the multiple pathways in which TRPs may be involved, here we focus our attention on the ones involving small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases), summarizing the main processes associated with the metastatic cascade, such as migration, invasion and tumor vascularization. In the last decade, several studies have highlighted a bidirectional interplay between TRPs and small GTPases in cancer progression: TRP channels may affect small GTPases activity via both Ca2+-dependent or Ca2+-independent pathways, and, conversely, some small GTPases may affect TRP channels activity through the regulation of their intracellular trafficking to the plasma membrane or acting directly on channel gating. In particular, we will describe the interplay between TRPC1, TRPC5, TRPC6, TRPM4, TRPM7 or TRPV4, and Rho-like GTPases in regulating cell migration, the cooperation of TRPM2 and TRPV2 with Rho GTPases in increasing cell invasiveness and finally, the crosstalk between TRPC1, TRPC6, TRPM8, TRPV4 and both Rho- and Ras-like GTPases in inducing aberrant tumor vascularization.
Keywords: cancer hallmarks; invasion; metastasis; migration; molecular signaling; small guanosine triphosphatases; transient receptor potential channels; tumor vascularization.
Copyright © 2020 Chinigò, Fiorio Pla and Gkika.
Figures

References
-
- Adapala R. K., Thoppil R. J., Luther D. J., Paruchuri S., Meszaros J. G., Chilian W. M., et al. (2013). Cellular Cardiology TRPV4 Channels Mediate Cardiac Fi Broblast Differentiation by Integrating Mechanical and Soluble Signals. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 54, 45–52. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.10.016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adapala R. K., Thoppil R. J., Ghosh K., Cappelli H., Dudley A. C., Paruchuri S., et al. (2016). Activation of Mechanosensitive Ion Channel TRPV4 Normalizes Tumor Vasculature and Improves Cancer Therapy. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 35 (3), 314–322. 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31823da96d.Hydrogen - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

