The Role of Nociceptive Neurons in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
- PMID: 33133059
- PMCID: PMC7550422
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01984
The Role of Nociceptive Neurons in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
Abstract
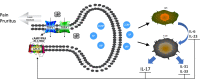
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. Emerging evidence shows that neurogenic inflammation, induced by nociceptive neurons and T helper 17 cell (Th17) responses, has a fundamental role in maintaining the changes in the immune system due to psoriasis. Nociceptive neurons, specific primary sensory nerves, have a multi-faceted role in detecting noxious stimuli, maintaining homeostasis, and regulating the immunity responses in the skin. Therefore, it is critical to understand the connections and interplay between the nociceptive neurons and the immune system in psoriasis. Here, we review works on the altered innervation that occurs in psoriasis. We examine how these distinct sensory neurons and their signal transducers participate in regulating inflammation. Numerous clinical studies report the dysfunction of nociceptive neurons in psoriasis. We discuss the mechanism behind the inconsistent activation of nociceptive neurons. Moreover, we review how neuropeptides, involved in regulating Th17 responses and the role of nociceptive neurons, regulate immunity in psoriasis. Understanding how nociceptive neurons regulate immune responses enhances our knowledge of the neuroimmunity involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and may form the basis for new approaches to treat it.
Keywords: TRPA1 and TRPV1 receptors; Th17; neurogenic inflammation; nociceptive neurons; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang and He.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

