Tumor-Secreted GRP78 Promotes the Establishment of a Pre-metastatic Niche in the Liver Microenvironment
- PMID: 33133103
- PMCID: PMC7550426
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584458
Tumor-Secreted GRP78 Promotes the Establishment of a Pre-metastatic Niche in the Liver Microenvironment
Abstract
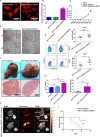
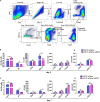
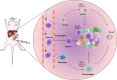
The liver is an immunologically tolerant organ and a common site of distant metastasis for various cancers. The expression levels of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) have been associated with tumor malignancy. Secretory GRP78 (sGRP78) released from tumor cells contributes to the establishment of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by regulating cytokine production in macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs). However, the role of sGRP78 on tumor cell colonization and metastasis in the liver remains unclear. Herein, we found that GRP78 was expressed at higher levels in the liver compared to other tissues and organs. We performed intravital imaging using a sGRP78-overexpressing breast cancer cell line (E0771) and found that sGRP78 interacted with dendritic cells (DCs) and F4/80+ macrophages in the liver. Importantly, sGRP78 overexpression inhibited DC activation and induced M2-like polarization in F4/80+ macrophages. Moreover, sGRP78 overexpression enhanced TGF-β production in the liver. In conclusion, sGRP78 promotes tumor cell colonization in the liver by remodeling the tumor microenvironment and promoting immune tolerance. The ability of sGRP78-targeting strategies to prevent or treat liver metastasis should be further examined.
Keywords: dendritic cells; immunomodulation; liver pro-metastatic niche; macrophages; natural killers; tumor-secreted GRP78.
Copyright © 2020 Chen, Zheng, Yu, Liu, Li, Zhu, Zhang, Lei and Shen.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cell Surface GRP78 Accelerated Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration by Activating STAT3.PLoS One. 2015 May 14;10(5):e0125634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125634. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Apr 11;18(4):e0284594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284594. PMID: 25973748 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Cell surface GRP78 promotes stemness in normal and neoplastic cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 26;10(1):3474. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60269-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32103065 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer cells resistant to therapy promote cell surface relocalization of GRP78 which complexes with PI3K and enhances PI(3,4,5)P3 production.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e80071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080071. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244613 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose regulated protein 78: a critical link between tumor microenvironment and cancer hallmarks.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1826(1):13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.02.001. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22426159 Review.
-
Progress of IL-10 and liver metastasis.Cytokine. 2025 Jun;190:156932. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2025.156932. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Cytokine. 2025. PMID: 40168924 Review.
Cited by
-
Liver Metastasis in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Management.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 27;6(3):e70119. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70119. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40027151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secreted glucose regulated protein78 ameliorates DSS-induced mouse colitis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 26;14:986175. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.986175. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776831 Free PMC article.
-
Immune dynamics shaping pre-metastatic and metastatic niches in liver metastases: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 14;23(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02171-z. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39543660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSP70s in Breast Cancer: Promoters of Tumorigenesis and Potential Targets/Tools for Therapy.Cells. 2021 Dec 7;10(12):3446. doi: 10.3390/cells10123446. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hepatic Pre-Metastatic Niche.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 31;14(15):3731. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153731. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

