Organ-Specific Effects of Low Dose Radiation Exposure: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 33133150
- PMCID: PMC7565684
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.566244
Organ-Specific Effects of Low Dose Radiation Exposure: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
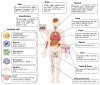
Ionizing radiation (IR) is a high-energy radiation whose biological effects depend on the irradiation doses. Low-dose radiation (LDR) is delivered during medical diagnoses or by an exposure to radioactive elements and has been linked to the occurrence of chronic diseases, such as leukemia and cardiovascular diseases. Though epidemiological research is indispensable for predicting and dealing with LDR-induced abnormalities in individuals exposed to LDR, little is known about epidemiological markers of LDR exposure. Moreover, difference in the LDR-induced molecular events in each organ has been an obstacle to a thorough investigation of the LDR effects and a validation of the experimental results in in vivo models. In this review, we summarized the recent reports on LDR-induced risk of organ-specifically arranged the alterations for a comprehensive understanding of the biological effects of LDR. We suggested that LDR basically caused the accumulation of DNA damages, controlled systemic immune systems, induced oxidative damages on peripheral organs, and even benefited the viability in some organs. Furthermore, we concluded that understanding of organ-specific responses and the biological markers involved in the responses is needed to investigate the precise biological effects of LDR.
Keywords: animal model; biological marker; human; low-dose radiation; organ-specificity.
Copyright © 2020 Shin, Lee, Kang, Kim, Kim, Youn, Jin, Seo and Youn.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma Proteins As Biodosimetric Markers of Low-Dose Radiation in Mice.Dose Response. 2021 May 10;19(2):15593258211016257. doi: 10.1177/15593258211016257. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. Dose Response. 2021. PMID: 33994891 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Biological Effects of Low-Dose Radiation in China.Dose Response. 2019 Feb 26;17(1):1559325819833488. doi: 10.1177/1559325819833488. eCollection 2019 Jan-Mar. Dose Response. 2019. PMID: 30833876 Free PMC article.
-
Possible association of G6PC2 and MUC6 induced by low‑dose‑rate irradiation in mouse intestine with inflammatory bowel disease.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jul;30(1):127. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13251. Epub 2024 May 24. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38785154 Free PMC article.
-
Re-evaluation of the linear no-threshold (LNT) model using new paradigms and modern molecular studies.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Mar 1;301:54-67. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.11.013. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30763548 Review.
-
p53-mediated metabolic response to low doses of ionizing radiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(6):934-940. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.2142983. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 36357962 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of low dose ionizing radiation against cancer, dementia, and diabetes: evidences from epidemiological, clinical, and preclinical studies.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Mar;50(3):2823-2834. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-08211-5. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36595119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monte Carlo methods to assess biological response to radiation in peripheral organs and in critical organs near the target.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024 Dec 4;29(5):638-648. doi: 10.5603/rpor.103525. eCollection 2024. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2024. PMID: 39759550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effects of UVB and Ionizing Radiation on Human Non-Malignant Cells: Implications for Ozone Depletion and Secondary Cosmic Radiation Exposure.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 6;15(4):536. doi: 10.3390/biom15040536. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305266 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing verifiable oncological imaging by quality assurance and optimization (i‑Violin) : Protocol for a European multicenter study.Radiologie (Heidelb). 2024 Nov;64(Suppl 1):160-165. doi: 10.1007/s00117-024-01389-8. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39477833 Free PMC article.
-
Population Studies and Molecular Mechanisms of Human Radioadaptive Capabilities: Is It Time to Rethink Radiation Safety Standards?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 18;25(24):13543. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413543. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bae S., Kim K., Cha H. J., Choi Y., Shin S. H., An I. -S., et al. . (2015). Low-dose γ-irradiation induces dual radio-adaptive responses depending on the post-irradiation time by altering microRNA expression profiles in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 35, 227–237. 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1994, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bakshi M. V., Azimzadeh O., Barjaktarovic Z., Kempf S. J., Merl-Pham J., Hauck S. M., et al. . (2015). Total body exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation induces long-term alterations to the liver proteome of neonatally exposed mice. J. Proteome Res. 14, 366–373. 10.1021/pr500890n, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

