Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Two Sibling Species of Parasitic Roundworms, Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta
- PMID: 33133162
- PMCID: PMC7578395
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.573395
Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Two Sibling Species of Parasitic Roundworms, Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta
Abstract
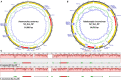
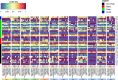
Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta are among the two most pathogenic internal parasitic nematodes infecting small ruminants, such as sheep and goats, and are a global animal health issue. Accurate identification and delineation of Haemonchidae species is essential for development of diagnostic and control strategies with high resolution for Trichostrongyloidea infection in ruminants. Here, we describe in detail and compare the complete mitochondrial (mt) genomes of the New Zealand H. contortus and T. circumcincta field strains to improve our understanding of species- and strain-level evolution in these closely related roundworms. In the present study, we performed extensive comparative bioinformatics analyses on the recently sequenced complete mt genomes of the New Zealand H. contortus NZ_Hco_NP and T. circumcincta NZ_Teci_NP field strains. Amino acid sequences inferred from individual genes of each of the two mt genomes were compared, concatenated and subjected to phylogenetic analysis using Bayesian inference (BI), Maximum Likelihood (ML), and Maximum Parsimony (MP). The AT-rich mt genomes of H. contortus NZ_Hco_NP and T. circumcincta NZ_Teci_NP are 14,001 bp (A+T content of 77.4%) and 14,081 bp (A+T content of 77.3%) in size, respectively. All 36 of the typical nematode mt genes are transcribed in the forward direction in both species and comprise of 12 protein-encoding genes (PCGs), 2 ribosomal RNA (rrn) genes, and 22 transfer RNA (trn) genes. The secondary structures for the 22 trn genes and two rrn genes differ between H. contortus NZ_Hco_NP and T. circumcincta NZ_Teci_NP, however the gene arrangements of both are consistent with other Trichostrongylidea sequenced to date. Comparative analyses of the complete mitochondrial nucleotide sequences, PCGs, A+T rich and non-coding repeat regions of H. contortus NZ_Hco_NP and T. circumcincta NZ_Teci_NP further reinforces the high levels of diversity and gene flow observed among Trichostrongylidea, and supports their potential as ideal markers for strain-level identification from different hosts and geographical regions with high resolution for future studies. The complete mt genomes of H. contortus NZ_Hco_NP and T. circumcincta NZ_Teci_NP presented here provide useful novel markers for further studies of the meta-population connectivity and the genetic mechanisms driving evolution in nematode species.
Keywords: Haemonchus contortus; Teladorsagia circumcincta; anthelmintic-susceptible; helminth; mitochondrial genome; parasite.
Copyright © 2020 Palevich, Maclean, Choi and Mitreva.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of the New Zealand parasitic roundworm Teladorsagia circumcincta (Trichostrongyloidea: Haemonchidae) field strain NZ_Teci_NP.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019 Sep 6;4(2):2869-2871. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1660241. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019. PMID: 33365767 Free PMC article.
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of the New Zealand parasitic roundworm Haemonchus contortus (Trichostrongyloidea: Haemonchidae) field strain NZ_Hco_NP.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019 Jul 12;4(2):2208-2210. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1624634. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019. PMID: 33365477 Free PMC article.
-
Development and field application of metabarcoding-adapted mt-ND4 markers shows substantial gene flow and varying local pressures on Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta populations in the UK.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 2;20(7):e0327254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327254. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40601687 Free PMC article.
-
Triple lectin staining of trichostrongyle eggs from naturally infected small ruminants.Vet Parasitol. 2021 May;293:109418. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109418. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Vet Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33866048
-
Understanding Haemonchus contortus Better Through Genomics and Transcriptomics.Adv Parasitol. 2016;93:519-67. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Adv Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27238012 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphology, Molecular Characterization, and Phylogeny of Travassosius rufus Khalil, 1922 (Strongylidea: Trichostrongylidae), a Parasite from Endangered Sino-Mongolian Beaver (Castor fiber birulai) in Xinjiang, China.Animals (Basel). 2025 May 6;15(9):1339. doi: 10.3390/ani15091339. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40362155 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and Reconstructing Helminth Mitochondrial Genomes Directly from Genomic Next-Generation Sequencing Data.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2369:27-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1681-9_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34313982
-
Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of the New Zealand parasitic blowfly Calliphora vicina (Insecta: Diptera: Calliphoridae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Mar 26;6(3):1270-1272. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1906775. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021. PMID: 33829105 Free PMC article.
-
Morphometry and Molecular Identification of Haemonchus Cobb, 1898 (Trichostrongylidae: Nematoda) Isolates from Small Ruminants in Tanzania Based on Mitochondrial cox 1 and rRNA-ITS genes.J Parasitol Res. 2023 Jan 16;2023:1923804. doi: 10.1155/2023/1923804. eCollection 2023. J Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 36698385 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted Multimodal Metabolomics Investigation of the Haemonchus contortus Exsheathment Secretome.Cells. 2022 Aug 15;11(16):2525. doi: 10.3390/cells11162525. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews S. (2010). FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Cambridge: Babraham Bioinformatics, Babraham Institute.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

