Docking Studies on Potential Mechanisms for Decreasing Insulin Resistance by the Tangzhiqing Herbal Formula
- PMID: 33133211
- PMCID: PMC7568782
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1057648
Docking Studies on Potential Mechanisms for Decreasing Insulin Resistance by the Tangzhiqing Herbal Formula
Abstract
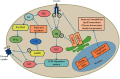
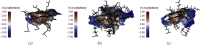
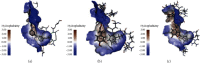
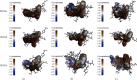
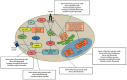
Insulin resistance (IR) is considered as one of the principal pathways of type 2 diabetes mellitus pathogenesis and is associated with a series of abnormal signaling pathways. Tangzhiqing (TZQ) herbal formula is a well-known antidiabetic traditional Chinese medicine and has been used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus and prediabetes for many years in China. We selected 13 natural products as representative compounds of the main active components in TZQ to investigate the interaction of these natural products with key signal proteins associated with IR using two different docking calculations. Salvianolic acids A and C (phenolic acids from Salvia miltiorrhiza), rutin (a flavonoid from Morus alba), paeoniflorin (a saponin from Paeonia lactiflora), and quercitrin (a flavonoid from Crataegus pinnatifida) showed great docking abilities towards multiple target proteins. These results have contributed to a clearer understanding regarding the regulation mechanism of TZQ on IR and have provided direction for further pharmacological studies.
Copyright © 2020 Jia Hao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

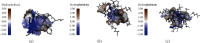

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

